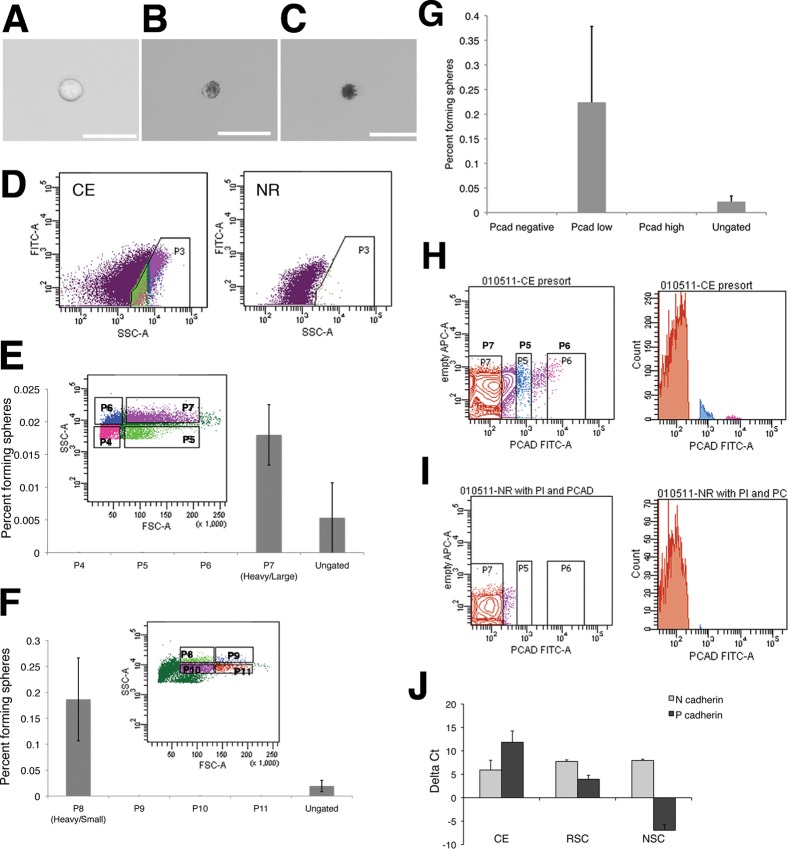
Fig. 1. RSCs can be isolated from ciliary epithelial (CE) cells using forward and side scatter and express the surface adhesion molecule P-cadherin.
CE dissection yields a variety of cell types: single non-pigmented cells are present (A) along with (B) lightly pigmented, and (C) heavily pigmented cells. Scale bars represent 25 µm. (D) Pigmented cells from dissociated CE make up a population with high side scatter that is not present in dissociated neural retina (NR). (E) This pigmented cell population was divided into 4 quadrants, of which only one gave rise to RSC colonies. (F) The population of large, heavily pigmented cells (P7) was subdivided into 4 new quadrants and RSCs colonies formed only from the smaller, most heavily pigmented cells. Cells were plated at clonal density (10 cells/µL) for colony forming assays. Error bars represent s.e.m., N = 3 for each.. Dissociated CE cells were immunostained for P-cadherin. Cells were divided into negative (P7), low (P5), and high (P6) P-cadherin level (G), FITC intensity along horizontal axis), which was not present in the secondary-only controls. (H) A histogram of cell counts for sorting of dissociated CE cells, while sorting dissociated NR (I) confirms that gate P7 is sorting for P-cadherin-negative cells, as NR cells do not express P-cadherin. All RSC colonies are derived from P-cadherin-low cells, N = 2. Freshly isolated CE expresses high levels of mRNA for P-cadherin, expressed in the pigmented CE and N-cadherin, expressed in the non-pigmented layer. (J) RSC colonies are derived from pigmented CE cells, but also express high levels of both cadherins as spheres are a mix of pigmented RSCs and non-pigmented progenitors. Data shown are deltaCt compared to the endogenous control rplp0 ± s.e.m., N = 2 or 3.