Fig. 5. Electron-microscopic analysis of extracellular components containing CD9 and CD81.
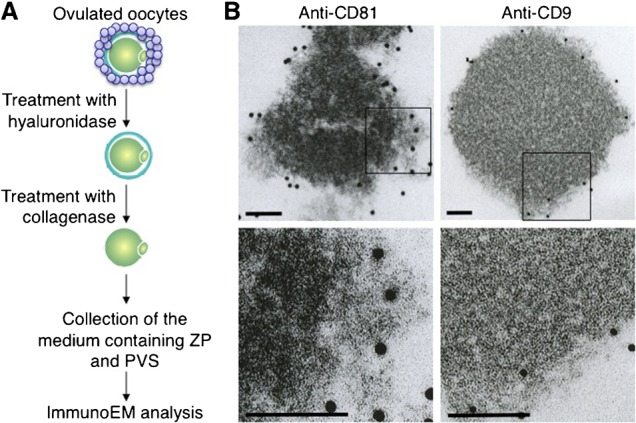
(A) Experimental flow for observing CD9-containing or CD81-containing extracellular structures. Oocytes were collected from oviducts of superovulated female mice, and cumulus cells were removed from oocytes by treatment with hyaluronidase. After ZP removal by collagenase, extracellular components containing ZP and PVS were collected, reacted with anti-CD9 or anti-CD81, and then incubated with 10 nm colloidal gold particles coupled to the secondary Abs for 1 hour at room temperature. The materials conjugated with the gold particles were spun down at 3,000 rpm for 10 min at room temperature, and the precipitates were washed with TYH medium three times. The final precipitates were fixed and subjected to electron-microscopic analysis. (B) Electron-microscopic analysis of materials bound to the gold particles. In each panel, boxes in the middle set of panels were enlarged and shown below. In each panel, scale bars: 100 nm.
