Fig. 8. Schematic representation of the distribution of CD81 and CD9 in oocytes upon fertilization.
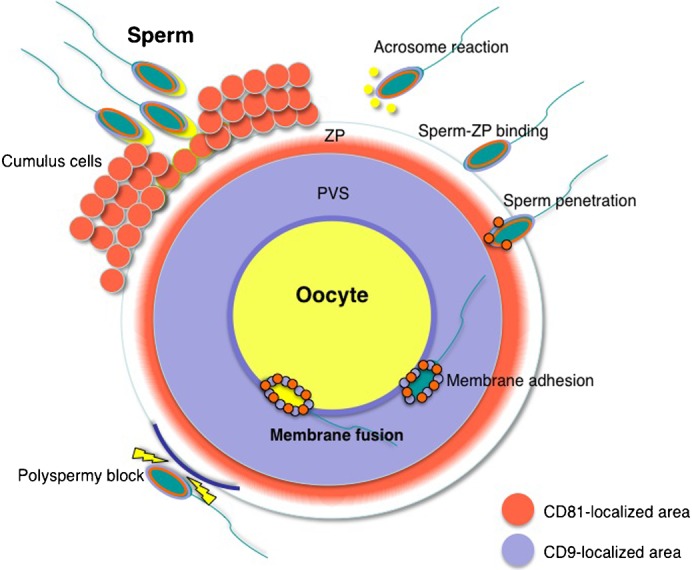
In fertilization, a sperm first interacts with cumulus cells. After the sperm has separated the cumulus cells from an oocyte by its own enzymatic activities, it commences an acrosomal reaction and then adheres to ZP (‘sperm-ZP binding’) (Jin et al., 2011). After sperm-ZP binding, the sperm penetrates the ZP and adheres to the oocyte cell membrane. At this time, membrane fusion occurs between the sperm and oocyte. Once a sperm has fused to the oocyte cell membrane, cortical granule exudates cause ZP modification (‘zona hardening’) to block polyspermic penetration. Upon fertilization, CD81 localizes in the inner region of the ZP, whereas CD9 localizes at the PVS. When the sperm penetrates the PVS, CD81 and CD9 molecules appear to adhere to the sperm surface via exosomes (Miyado et al., 2008; Ito et al., 2010; Kawano et al., 2011). Orange area, CD81-localized area; light blue area, CD9-localized area. ZP, zona pellucida; PVS, perivitelline space.
