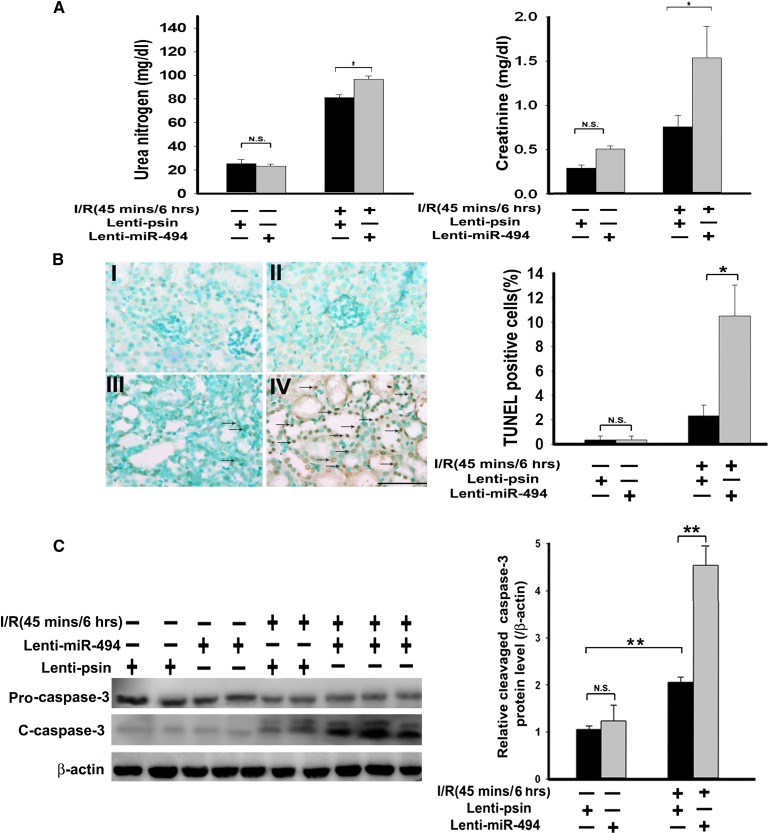
Figure 4.
miR-494 overexpression decreases kidney function and increases renal apoptosis in mice. (A) Kidney functions assessed with or without miR-494 infusion after I/R injury. Bilateral renal arteries were clamped for 45 minutes, and serum urea nitrogen and creatinine levels were measured 6 hours after reperfusion or sham surgery. Values are means ± SEM; n=7 animals/group. *P<0.05 compared with control groups. (B) Apoptotic kidney cells in mice infused with or without miR-494 using in vivo TUNEL staining. Without (I and III) or with (II and IV) infused miR-494, mice underwent a sham operation (I and II) or 45 minutes of renal clamping to induce ischemia followed by 6 hours of reperfusion (III and IV). TUNEL staining of representative kidney sections from each experimental group are shown. Colocalization of blue and brown staining in nuclei reflects apoptotic cells that are indicated with arrows. Scale bar, 50 μm. Proportions of TUNEL-positive renal epithelial nuclei to total nuclei in mice infused with or without miR-494 and subjected to the sham operation or I/R injury are shown. *P<0.05 (n=7 animals/group). (C) Active caspase-3 protein expression in mouse kidney with or without lenti–miR-494 infection. Kidney lysates of mice subjected to the sham operation or I/R injury were probed with specific antibody against the uncleaved, pro–caspase-3 and cleaved, active form of caspase-3. Scanning densitometry was used for semiquantitative analysis and compared with β-actin levels. Values are means ± SEM from three experiments. **P<0.01 (n=3).