Figure 2. Rationale for using HERAM to identify heritable candidate regions for a disease.
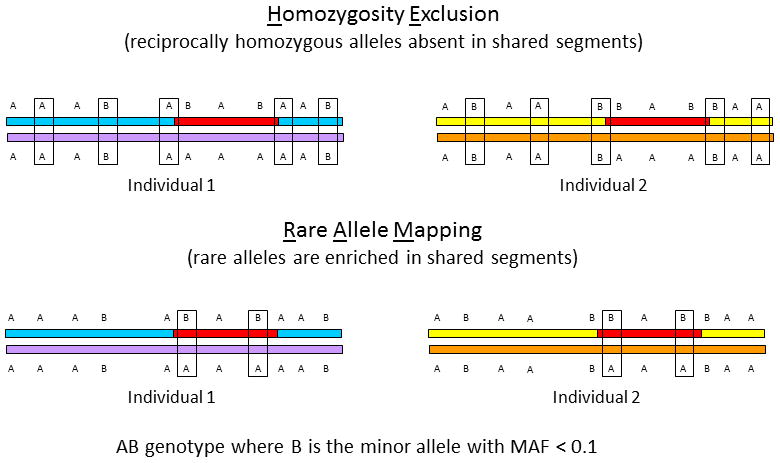
HERAM is based on two ideas. First, within a shared genomic segment (red segment), alleles will never be reciprocally homozygous (that is, AA in one individual and BB in another) at the same SNP. In the upper panel, reciprocally homozygous alleles are boxed. Note that there are no boxes in the shared segment and that boxes define the boundaries of the shared segment. Second, rare-shared alleles are enriched in shared genomic segments. These are shown in the lower diagram with boxed AB genotypes, where the MAF of the B allele is <0.1. Regions that are both devoid of exclusionary reciprocally homozygous SNPs and enriched for rare shared alleles are identical-by-state, and likely identical-by-descent when the segment is large (≥ 6 cM) and individuals are distantly related. MAF= minor allele frequency.
