Figure 2. Cardioprotective signaling: all roads lead to mitochondria.
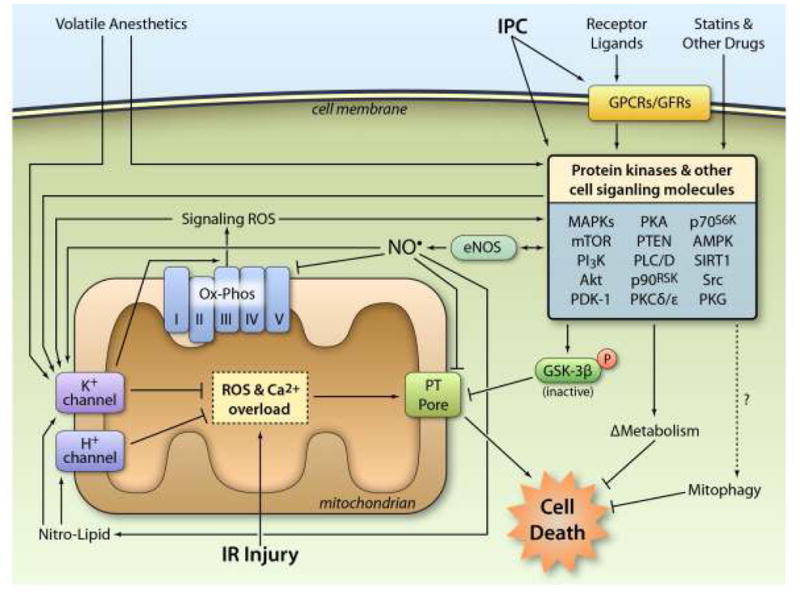
IPC either directly or indirectly (via G-protein coupled receptors or growth factor receptors) activates numerous protein kinases and other cell signaling molecules, including the generation of ROS for signaling purposes. These signals filter through a limited number of downstream mediators including: (i) eNOS generation of NO•, (ii) phosphorylation and inhibition of GSK-3β, (iii) changes in metabolism (iv) activation of mitophagy. At the mitochondrial level, many of these signals converge on the opening of mKATP and mBK channels, and the activation of H+ channels, both of which inhibit the PT pore directly, or inhibit the events leading up to its opening. Volatile anesthetics also trigger mitochondrial K+ channel opening and recruit many of the same kinase signals as IPC. Other drugs such as statins can also activate kinases in the RISK pathway. Together, these events inhibit cell death during subsequent IR injury. See text for more details. (Illustration Credit: Ben Smith).
