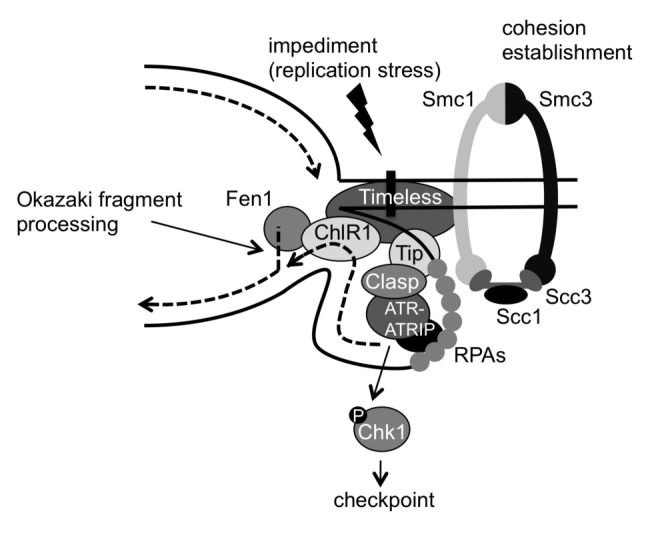
Figure 1. Model for the roles of the fork protection complex (FPC) in checkpoint activation, DNA replication and sister chromatid cohesion. The replication fork can pause or stall at a variety of impediments throughout the genome. These impediments may include DNA damage, fork barriers, DNA secondary structures, proteins bound on DNA and even cohesin complexes. ssDNA accumulated at stalled forks is coated by RPA bound by ATR-ATRIP. RPA is also bound by Tipin, which then recruits the checkpoint mediator Claspin, resulting in activation of the ATR-Chk1-dependent checkpoint. Tipin also recruits Timeless, which stabilizes cohesin subunits on chromatin. Timeless interacts with ChlR1 DNA helicase, which stimulates Fen1 activity for Okazaki fragment processing. This promotes efficient lagging-strand DNA synthesis and minimizes the size of the replication loop at the lagging strand, thereby promoting efficient progression of replication forks through cohesin rings.
