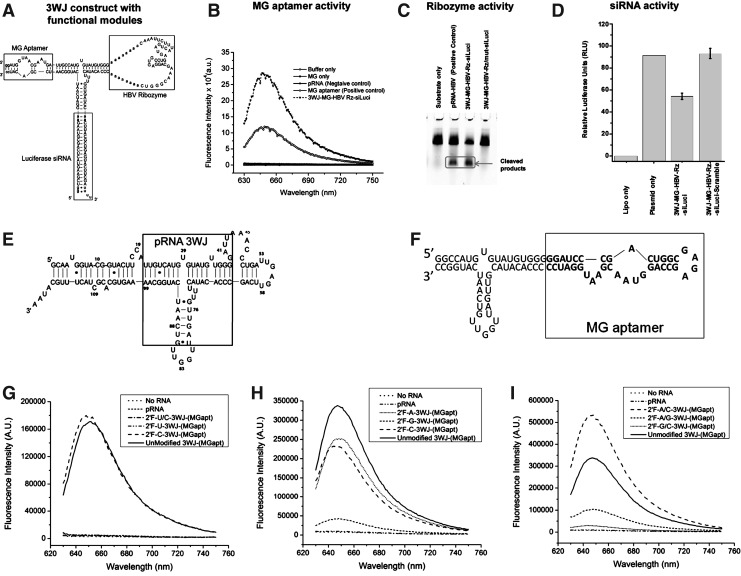
FIG. 1.
(A) Design and sequence of an RNA nanoparticle harboring a malachite green (MG) aptamer, hepatitis B virus (HBV) ribozyme, and small interfering RNA(siRNA) targeting firefly luciferase. (B) Functional assay of the MG aptamer incorporated in the 3-way junction (3WJ) nanoparticle. MG fluorescence was measured using 615 nm excitation. (C) Catalytic activity of the HBV ribozyme. Cleaved products are boxed. (D) Dual-luciferase assay for target gene knockdown of the firefly luciferase gene. Relative luciferase activity is obtained by normalizing the firefly luciferase expression to the renilla luciferase internal control. Error bars represent the standard deviation of 3 trials. The RNA sequence and structure of the wild type packaging RNA (pRNA) (E) and pRNA-3WJ-(MGapt) (F). (G-I) The binding and fluorescence spectra of pRNA-3WJ-(MGapt) made with various 2′F-modified rNTPs (ATP, CTP, GTP, UTP) including a comparison of UTP and CTP binding (G); 2′F-ATP, 2′F-GTP, and 2′F-CTP (H); as well as the structures with multiple modified nucleotides (I). This shows that the modification of UTP or GTPs deactivates the MG aptamer and no binding of MG occurs.