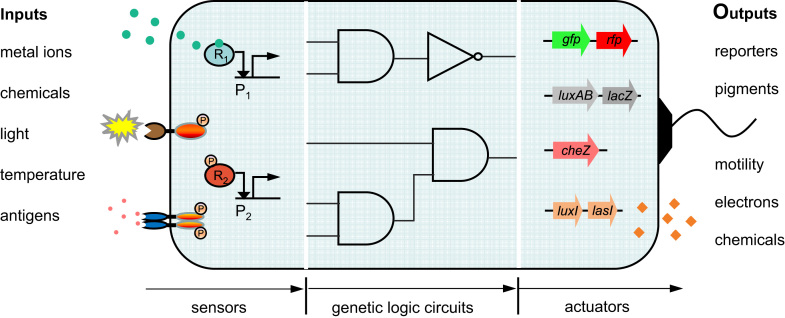
Fig. 1.
Architecture of a synthetic modular cell-based biosensor. The cellular sensor comprises three interconnected and exchangeable modules, i.e. the input sensors, the internal genetic information processing circuits and the output actuators. The cells are engineered using various natural or synthetic sensors such as sensor kinases or intracellular receptor proteins to detect environmental signals and genetic circuits such as AND and NOT logic gates to modulate and integrate these multiple input signals. The programmed cells can then initiate customized responses by activating different output genes according to the logic decision transmitted upstream. Adapted with permission from Wang and Buck (2012).