Figure 4. Test case for linked predicted binding sites forming a FAD-binding site.
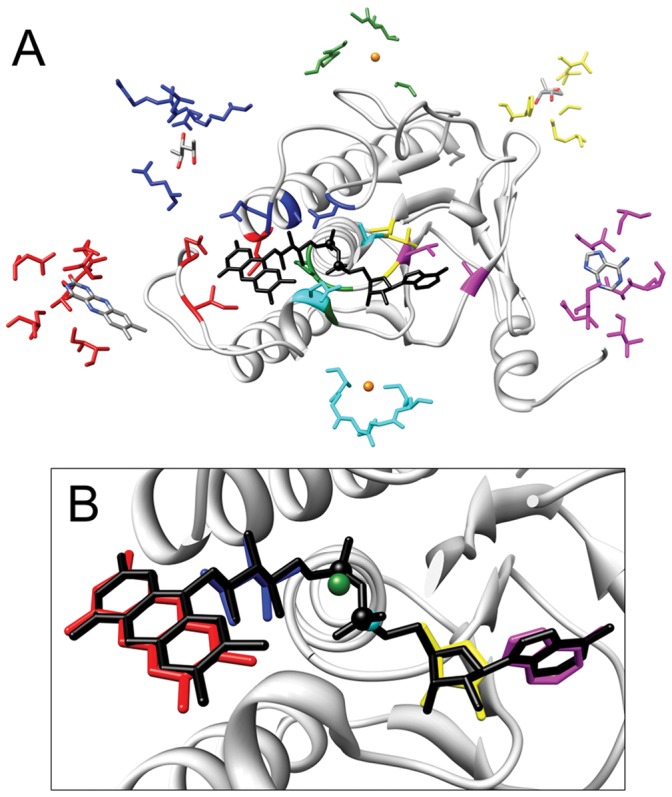
Top ranked prediction for the binding site of the FAD molecule bound by the subunit F of the Alkyl hydroperoxide reductase from S. typhymurium (PDB code 1hyu). A) Structure of the reductase (residues from 1 and 197 and from 325 to 453 are not shown for convenience) with the structures of the template binding sites matching with reductase residues (red: I46, N48, V290, Q289 of the thioredoxin reductase from H. pylori (PDB: 3ish) binding a flavin module; blue: D287, Q295, S299 of the thioredoxin reductase from S. cerevisiae (PDB: 3itj) binding a ribose; cyan: K112, G109, S108 of the human RNA helicase DDX20 (PDB: 3b7g) binding a phosphate; green: G10, P11, G38, G138 of the 2-oxoglutarate dehydrogenase E3 component from T. thermophilus (PDB: 2yqu) binding a phosphate; yellow: G10, A137, T138 of a putative monoxygenase from S. aureus (PDB: 3d1c) binding a ribose; magenta: I11, A122, T157 of the gernaylgeranyl reductase from S. acidocaldarius (PDB: 3atr) binding an adenine). The modules bound by the template binding sites are colored by atom type (grey for Carbon, blue for Nitrogen, Red for Oxygen and Orange for Phosphorus). Matching residues are depicted with the same color. B) The prediction is composed of predicted binding sites for nucleotide modules: predicted modules are colored as their binding sites in A. The FAD molecule bound by the protein is colored in black.
