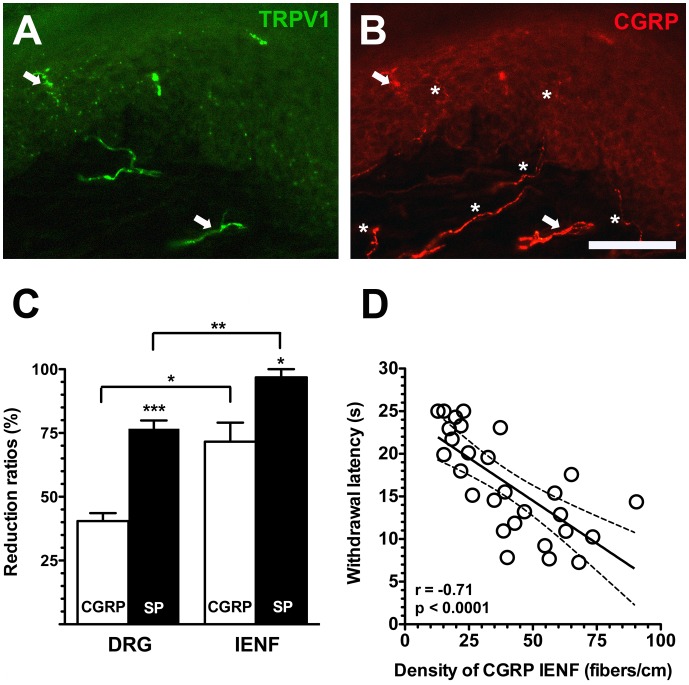
Figure 7. Differential extents of depletion of calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) and substance P (SP) neurons and intraepidermal nerve fibers (IENFs) in resiniferatoxin (RTX)-induced neuropathy.
(A, B) Double-labeling immunofluorescent staining was performed with anti-transient receptor potential vanilloid subtype 1 (TRPV1, A in green) and calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP, B in red) on the footpad skin of the vehicle group. There were limited CGRP(+) IENFs were coexpressed TRPV1 (arrow in A and B) and mostly CGRP(+) IENFs were TRPV1(−) IENFs (asterisk in B). (C) The graph shows different reduction ratios on the density of IENFs and dorsal root ganglia (DRGs) of different phenotypes: SP (filled bars, n = 5) and CGRP (open bars, n = 5). (D) The graph shows the correlation of CGRP(+) IENFs and withdrawal latency on hot-plate test in RTX-induced neuropathy. Bar, 100 µm; *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001.