Figure 2. Dbh −/− mice are hypersensitive to cocaine-induced locomotion.
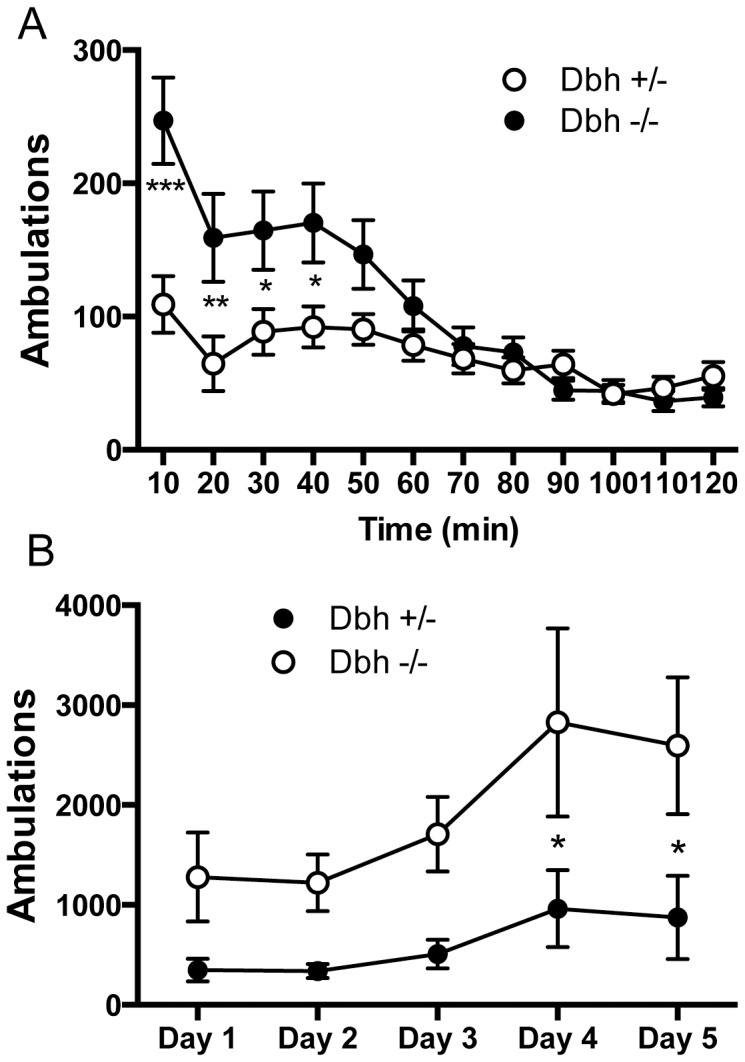
(A) Drug-naïve Dbh +/− (n = 9) and Dbh −/− mice (n = 8) were placed in automated locomotor activity chambers, injected with cocaine (15 mg/kg, i.p.) 30 minutes later, and locomotor activity was recorded for 2 hours. Shown are mean ± SEM ambulations (consecutive beam breaks). *** p<0.0001, ** p<0.01, * p<0.05 compared with Dbh −/− mice at that time point. (B) On each of the next 5 days, mice were administered saline (3 injections of 10 ml/kg, each injection spaced 2 hours apart). Ninety minutes after the last saline injection, mice were placed in automated locomotor activity chambers, injected with cocaine (15 mg/kg, i.p.) 30 minutes later, and locomotor activity was recorded for 2 hours. Shown are mean ± SEM ambulations (consecutive beam breaks) for the 2 hours following cocaine administration. * p<0.05 between genotypes for that day.
