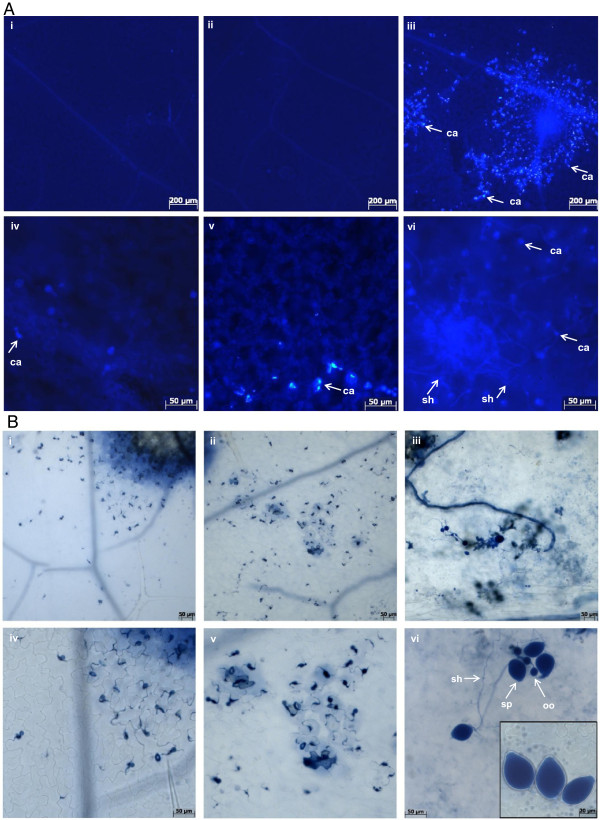
Figure 2.
Responses of the pss1 mutant following P. sojae infection. A, Leaves of 21 day old Col-0, pen1-1 and pss1 seedlings were inoculated with P. sojae zoospores and stained with aniline blue and visualized under a Zeiss Axioplan II compound microscope with ultraviolet epifluorescence [25]. (i) and (iv), Col-0; (ii) and (v), pen1-1; and (iii) and (vi), pss1 leaves that were stained with aniline blue to detect callose deposition 6 hours post inoculation (hpi) with P. sojae by epifluorescence of the aniline blue. (i-iii), 50X magnification; and (iv-vi), 200X magnification. Arrows indicate sites of callose deposition (ca) and secondary hyphae (sh). The experiment was repeated twice with similar results. B, Leaves of 21 day old Col-0, pen1-1 and pss1 seedlings were inoculated with P. sojae zoospores and stained with trypan blue and visualized under a Zeiss Axioplan II compound microscope under bright field illumination [23]. (i) and (iv), Col-0; (ii) and (v), pen1-1; and (iii) and (vi), pss1 leaves that were stained with trypan blue to detect cell death and fungal structures 7 days following inoculation with P. sojae zoospores. Arrows indicate reproductive structures, oogonia (oo), sporangia (sp) and secondary hyphae (sh), which were visible in infected pss1 leaves. (i-iii), 100X magnification; and (iv-vi), 200X magnification. The experiment was repeated twice with similar results.