Figure 4.
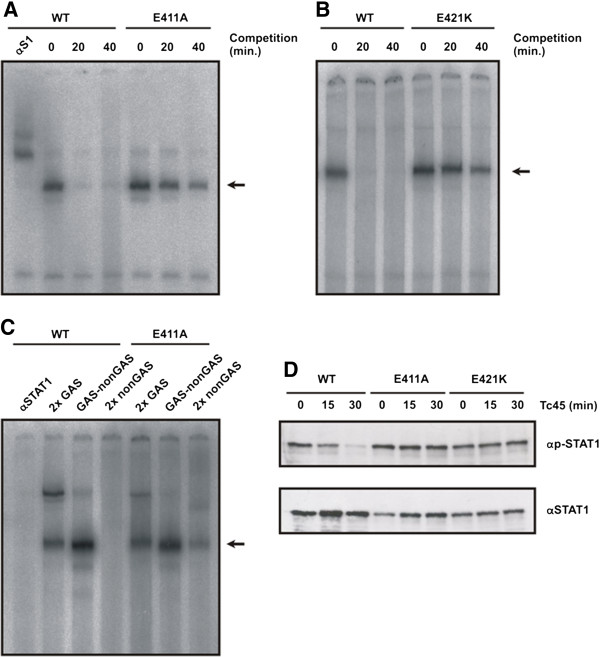
Replacement of glutamyl residues in position 411 or 421 results in STAT1 mutants with a decreased dissociation rate from DNA and high-affinity binding to non-canonical binding sites. (A) Comparison of the dissociation rates between STAT1-WT and STAT1-E411A on a DNA fragment containing a single STAT binding site (M67). Whole cell extracts from U3A cells were incubated with radioactively labeled DNA for 15 min and, subsequently, a 750-fold molar excess of unlabeled DNA was added for the durations indicated before the samples were loaded onto a polyacrylamide gel. In the first lane, anti-STAT1 antibody C-24 was present in the EMSA reaction for identification of STAT1-DNA complexes which are marked with an arrow. (B) Similar experiment as in (A), except that U3A cells expressing E421K were used. (C) Sequence requirements for binding of mutant STAT1 to DNA. Whole cell extracts from U3A cells expressing either STAT1-WT or the E411 mutant were incubated with various [32P]-labeled DNA molecules containing two single consensus GAS sites (2x GAS), a consensus and mutant GAS site in tandem arrangement (GAS-nonGAS) or two non-GAS sites (2x non-GAS). Lane 1 is similar to lane 2 except that the reaction additionally contained STAT1-specific antibody C-24 (αSTAT1). Note that wild-type STAT1 did not bind to 2x non-GAS, while the same DNA fragment exhibits a weak affinity for STAT1-E411A. The dimeric STAT1-DNA complexes are marked with an arrow. (D) An in vitro dephosphorylation assay shows that DNA-bound E411A and E421K are protected from Tc45-catalyzed inactivation. Whole cell extracts from reconstituted U3A cells were incubated with the recombinant Tc45 phosphatase for the indicated times and the reactions were then subsequently probed for phospho-STAT1 levels by means of Western blotting (αp-STAT1). The membrane was stripped and re-incubated with the pan-STAT1 antibody C-24 (αSTAT1).
