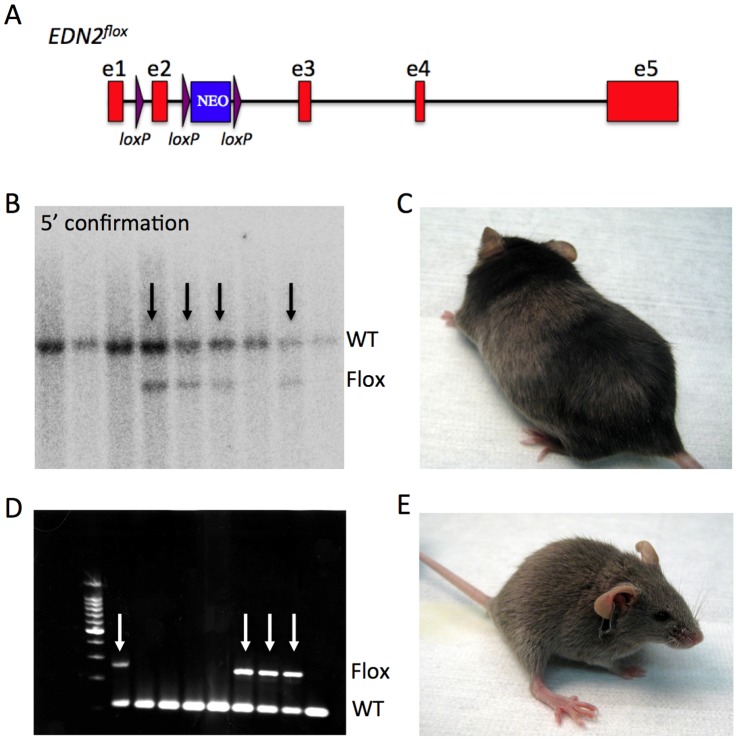
Figure 4. Generating a conditional allele of Edn2 directly in DBA/2J-derived ES cells.
(A) A targeting construct was generated that included loxP sites flanking exon 2 (e2) of the Edn2 gene. Exon 2 contains part of the key functional domain for Edn2, and removal of exon 2 induces a frameshift for protein translation (B) Correct targeting at the 5′ end of the Edn2 gene was assessed using Xba1 restriction digests and southern blotting. The presence of the Neomycin (NEO) selectable marker incorporates an additional Xba1 restriction enzyme site in the targeted allele, generating a 6.6 kb fragment (Flox) compared to the normal 8.7 kb fragment (WT). Black arrows indicate clones correctly targeted at the 5′ end. (C) An example of a chimeric mouse generated as a result of injection of targeted DBA/2J ES cell clones into C57BL/6J blastocysts. (D–E) Chimeric male mice were mated with DBA/2J females and offspring genotyped for the heterozygous presence of the loxP sites in intron 1 (WT = 481 bp, Flox = 631 bp, see Methods). White arrows indicate mice that carry the floxed allele of Edn2. (D). See methods for primer information. As expected, 100% of heterozygous mutant offspring had the DBA/2J coat color (dilute brown agouti, E).