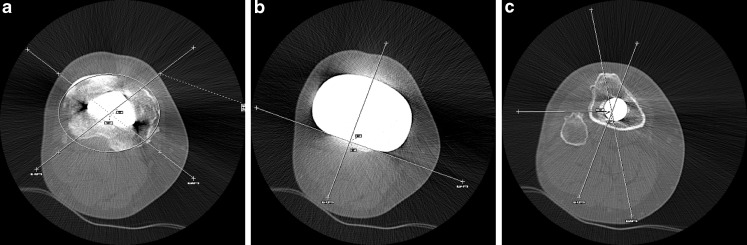
Fig. 1.
Tibial component rotational assessment using an axial CT in a 61-year-old male. a The geometric centre of the proximal tibial plateau is determined using an ellipse delineating the tibial plateau. b A line perpendicular to the posterior condylar axis of the tibial component is constructed. c The tibial component rotational angle is determined to be 14° of excessive internal rotation, by transposing the geometric centre as measured in A and the perpendicular line as measured in B to the tibial tuberosity slice and connecting the centre to the protuberant point of the tibial tubercle