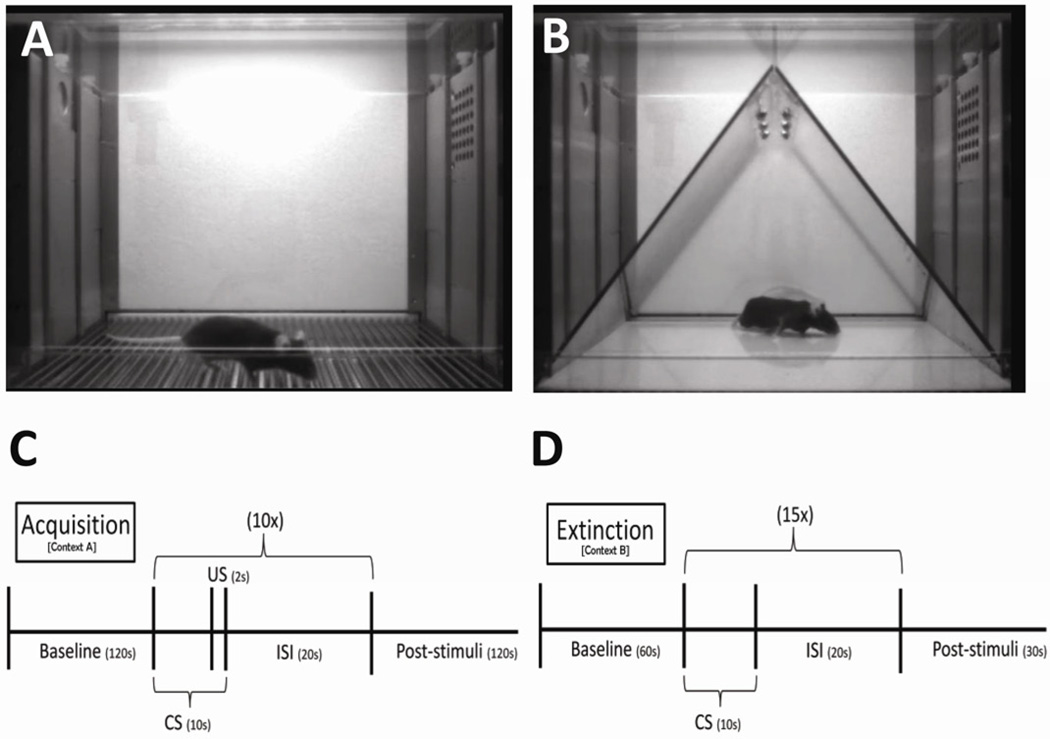
Fig. 2.
Day 1 (training) fear conditioning of WT and mGluR4−/− mice in ‘Context A’ (see methods). (A) Average baseline motion (arbitrary units) was recorded to assess general locomotor activity. Wild-type mice tended to be more active in the baseline period than mGluR4−/− mice. (B) Average motion (arbitrary units) during the shocks (the 10 shocks were averaged). (C) Percent time freezing during the entire training trial, which was analyzed using the following time periods: baseline (Bl), acquisition (Acq), and post-stimuli (Ps). Baseline consisted of a 2-minute period with no stimuli in which mice generally had zero freezing. Therefore freezing was not analyzed during this period. During the acquisition phase, mice received a total of ten tone-shock pairings that were administered at equal intervals. mGluR4−/− mice tended to freeze more than wild-type mice during minutes 5,6, and 7. The post-stimuli period represents the immediate freezing to the context after all tone-shocks ceased. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. Error bars represent SEM values.