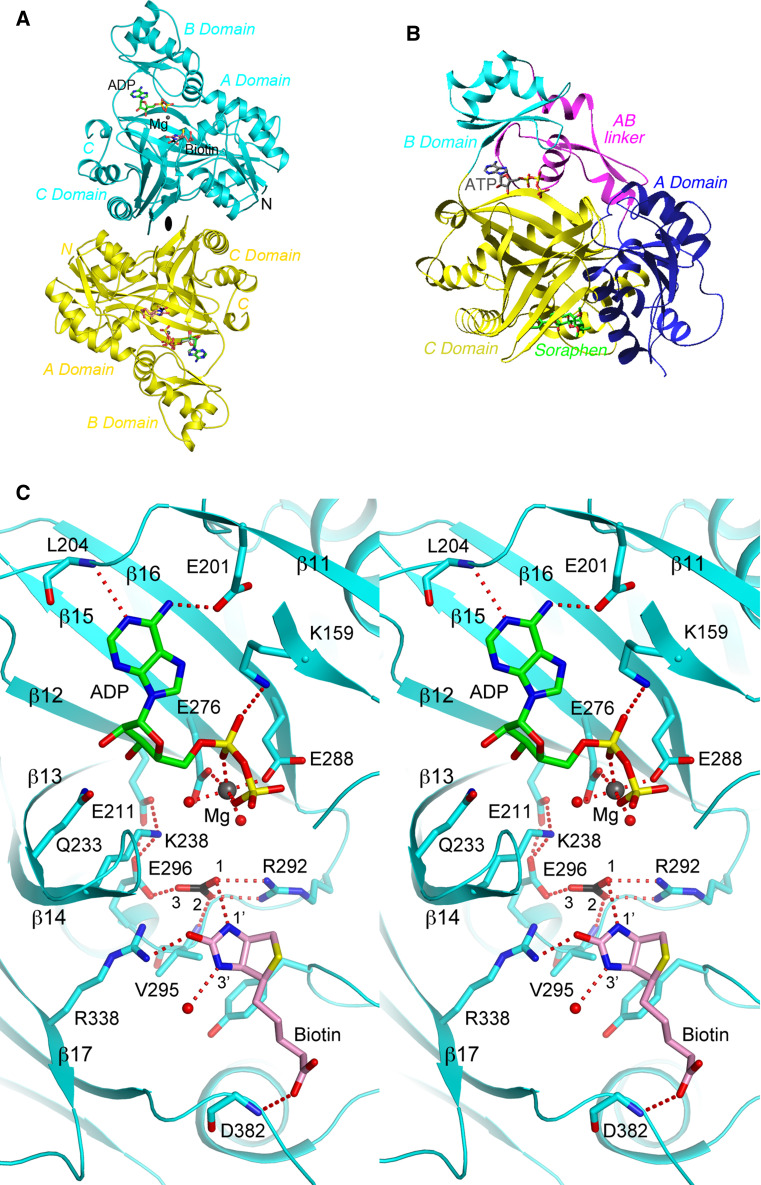
Fig. 4.
Structural information on the BC component. a Structure of the BC subunit dimer (cyan and yellow) of E. coli ACC in complex with MgADP, bicarbonate, and biotin [154]. The twofold axis of the dimer is indicated with the black oval. b Structure of the BC domain of yeast ACC in complex with the inhibitor soraphen A (green) [161]. The sub-domains of BC are given different colors. The bound position of ATP is also shown to indicate the location of the active site. The view is similar to that for the top monomer in a. c Stereo figure showing detailed interactions between MgADP, bicarbonate, and biotin with the active site of the E. coli BC subunit. Several segments of the protein, including the glycine-rich loop, are omitted for clarity. The structure figures were produced with the program PyMOL (www.pymol.org)