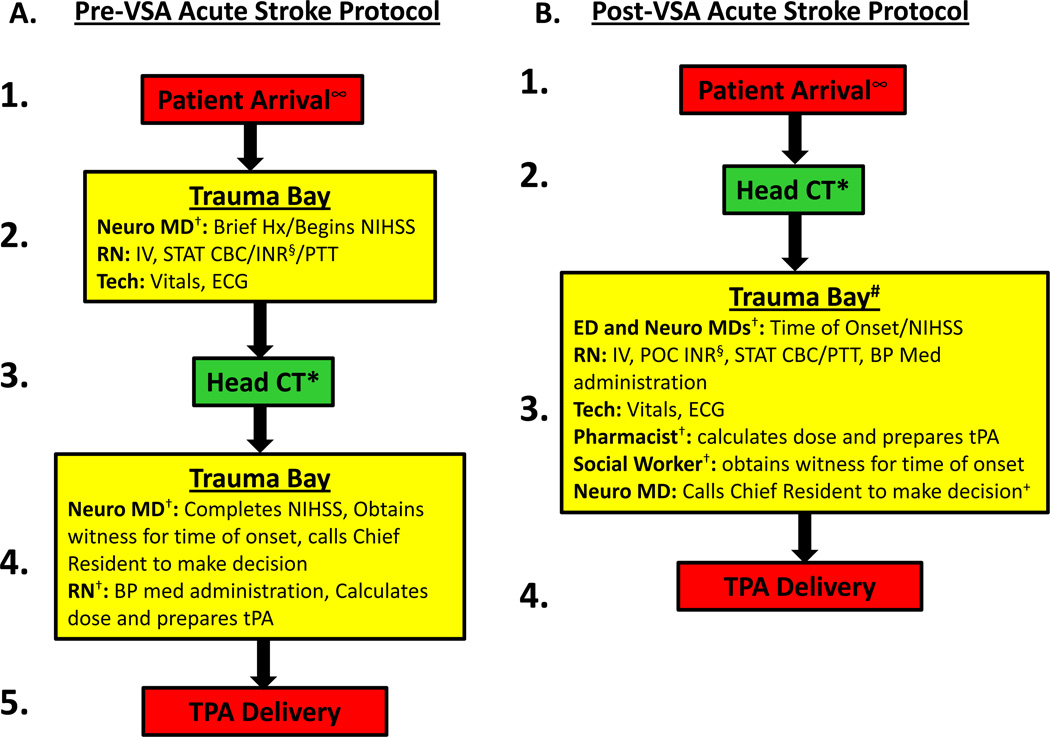
Figure. Acute stroke protocol pre-VSA (A) and post-VSA (B).
∞ EMS pre-notified the ED triage nurse of the patient’s arrival so that treating physicians and staff were waiting and ready to evaluate the patient immediately upon arrival. The patient could not be pre-registered and prior medical records could not be investigated prior to patient arrival as EMS was not allowed to give patient identifiers via radio due to violation of patient privacy.
† Serial tasks were changed to In-parallel.
* Head CT moved to first step in the protocol.
# Transport from CT to trauma bay might be considered “time-wasteful”; however, three reasons prevented utilizing the CT scanner as the location for tPA delivery: (1) given the ED traffic and the demand for CT utilization, it was necessary to permit its use for other disease categories (such as trauma and others); (2) transport from CT scanner to trauma bay is about 30 seconds; and (3) the space and lighting for patient evaluation in the trauma bay are superior to that in the CT scanner room.
§ Point-of-Care INR sent (useful for patients suspected or known to be taking coumadin/warfarin).
+ Calling the Chief Resident might be considered “time-wasteful”; however, we ultimately decided that it “added value” by ensuring tPA administration was supervised by experienced physicians, ensuring safe and appropriate tPA delivery.
VSA=Value Stream Analysis; Neuro MD=neurology medical doctor; Hx=history; NIHSS=National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale; RN=registered nurse; Tech=patient care technician.