Fig. 5.
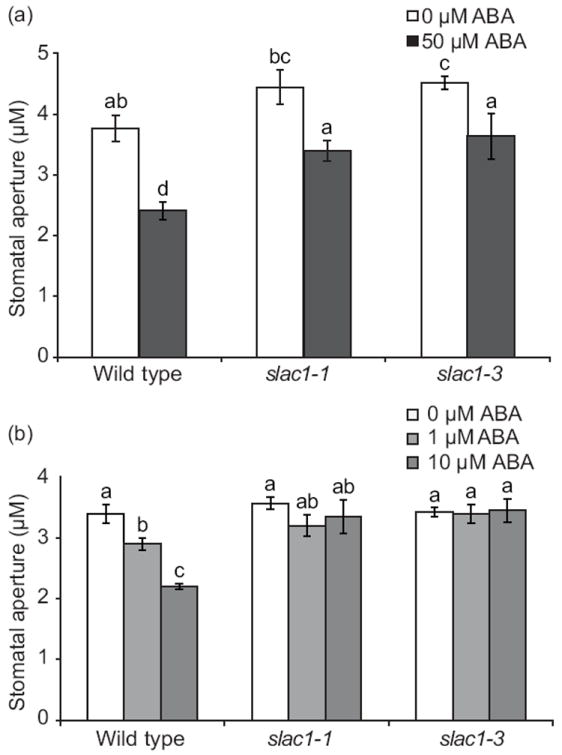
Partial abscisic acid (ABA)-induced stomatal closure in Arabidopsis slac1 mutants depends on ABA concentration and duration of ABA exposure. (a) Leaves of wild type, slac1-1, and slac1-3 were incubated in 0 μM ABA or 50 μM ABA for 3 h (±SEM, n = 20-33). (b) Impaired ABA-induced stomatal response in slac1-1 and slac1-3 mutants, at lower ABA concentrations (1 and 10 μM ABA) and reduced exposure time to ABA (1 h). ABA-induced stomatal closure in wild type, slac1-1, and slac1-3, intact leaf epidermis treated with the indicated ABA concentrations for 1 h (±SEM, n = 3 experiments, 30 stomata per condition per experiment). Experiments were conducted as genotype and [ABA] blind experiments. Letters refer to significant (P < 0.05) differences (ANOVA and LSD test).
