FIG. 1.
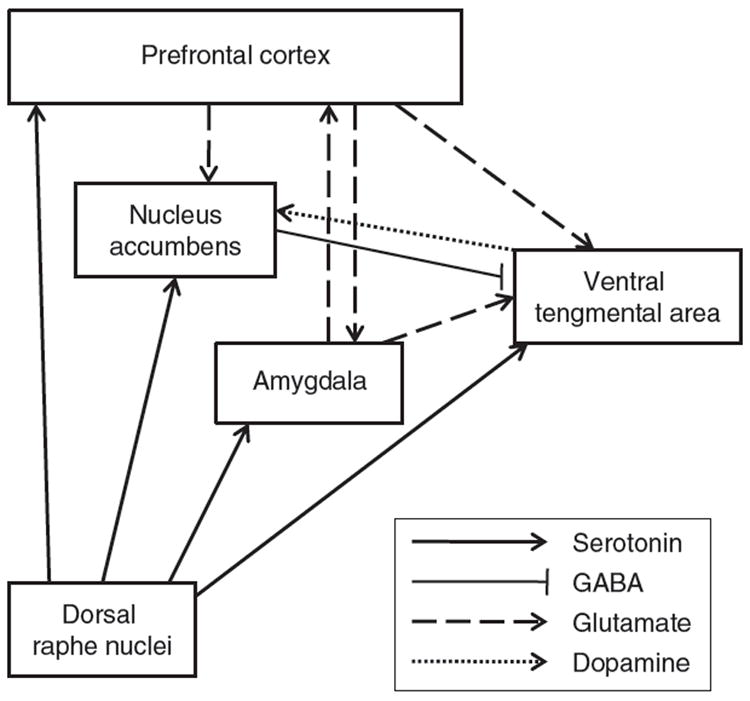
Schematic representation of the serotonergic neurocircuitry as it relates to the other neurotransmitter systems involved in alcohol dependence. Serotonergic neurons project to different reward brain regions such prefrontal cortex (PFC), nucleus accumbens (NAc), ventral tegmental area (VTA), and amygdala. The GABAergic NAc-VTA pathway contains 5-HT receptors at its terminal and controls the release of GABA, which in turn regulates the release of dopamine of the VTA-NAc pathway. The glutamatergic projections from the PFC targeting the NAc and VTA express 5-HT receptors at their terminals, which control the release of glutamate.
