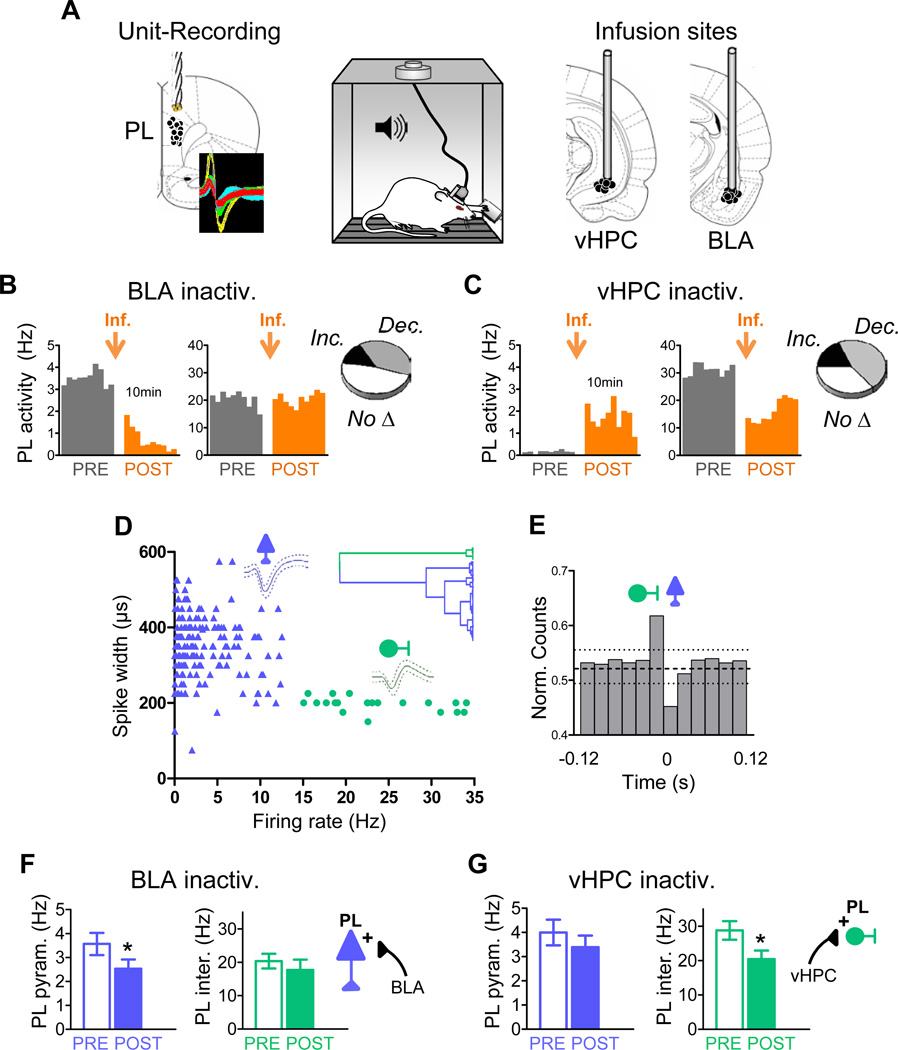
Figure 1. Basolateral amygdala and ventral hippocampus differentially modulate the spontaneous activity of prelimbic pyramidal neurons and interneurons after conditioning.
(A) Conditioned rats previously trained to press a lever to obtain food were implanted with unit recording electrodes in the prelimbic (PL) prefrontal cortex and locally infused with muscimol (MUS) in the basolateral amygdala (BLA) or ventral hippocampus (vHPC). Coronal drawings show the location of recording electrodes (left) and cannula injector tips (right). Inset shows example extracellular waveforms.
(B & C) Histograms show ten minutes of spontaneous PL firing rate of representative neurons before (grey) and after (orange) MUS infusion (orange arrow) into either the BLA (B) or vHPC (C) (bin width = 1 min). Delay between pre- and post-infusion recordings was between 2 h and several days. Insets illustrate the proportion of PL cells that significantly increased rate, decreased rate, or showed no significant changes.
(D) Classification of PL neurons into putative pyramidal excitatory cells (blue) and interneurons (green) based on waveform duration and firing rate. Dendrogram inset shows the unsupervised cluster analysis that identified two main clusters.
(E) Averaged cross-correlation analysis for 10 pairs of simultaneously recorded PL interneurons and pyramidal cells, illustrating inhibitory interactions between interneurons (reference cell, firing at 0) and pyramidal cells (binned spike count normalized to overall firing rate) (bin width = 20 ms). Dashed horizontal line indicates mean; dotted lines indicate 95% confidence intervals.
(F) BLA inactivation significantly decreased activity of PL pyramidal neurons (blue bars) without affecting activity of PL interneurons (green bars).
(G) vHPC inactivation significantly decreased the activity of PL interneurons without affecting activity of pyramidal neurons. In this and subsequent figures, error bars illustrate s.e.m.; *p<0.05.