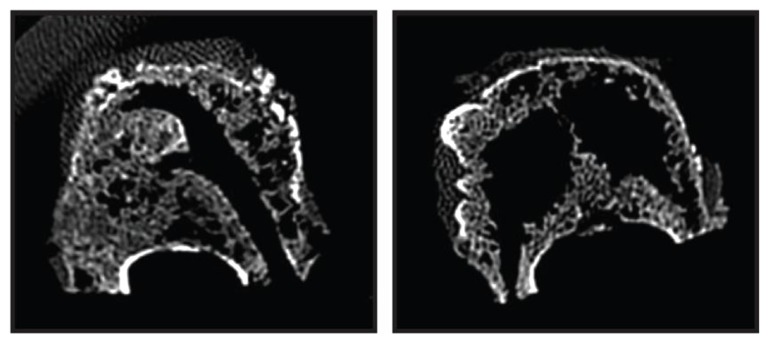
Figure 4.
Computed tomography images of vertebrae following cavity creation, prior to cement augmentation.
Notes: Discrete directional cavity created using the navigational MidLine Osteotome (DFINE, Inc, San Jose, CA) via a unipedicular approach during radiofrequency-targeted vertebral augmentation preserves more trabecular bone and creates preferential path(s) for targeted flow of ultrahigh-viscosity cement (left). Large cavities resulting from bipedicular balloon expansion reduce the amount of trabecular bone and area for cement interdigitation (right).