Abstract
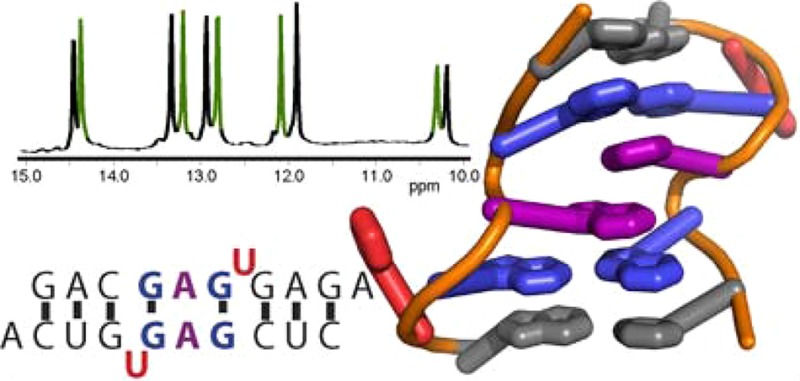
The RNA duplex, (5′GACGAGUGUCA)2, has two conformations in equilibrium. The nuclear magnetic resonance solution structure reveals that the major conformation of the loop, 5′GAGU/3′UGAG, is novel and contains two unusual Watson–Crick/Hoogsteen GG pairs with G residues in the syn conformation, two A residues stacked on each other in the center of the helix with inverted sugars, and two bulged-out U residues. The structure provides a benchmark for testing approaches for predicting local RNA structure and a sequence that allows the design of a unique arrangement of functional groups and/or a conformational switch into nucleic acids.
RNA performs a plethora of important functions in the cell,1 and it has been estimated that more than 75% of human DNA is transcribed into RNA.2 While a huge number of RNA sequences are known, there is a much smaller database of three-dimensional (3D) RNA structures. In contrast, only ∼5% of human DNA encodes protein, but the database of protein structures is large (http://www.pdb.org).3 That database has facilitated the development of accurate methods for predicting and designing 3D structures of proteins from sequence using homology modeling and/or force fields.4−7 These methods can also be applied to RNA8−13 and will become more accurate as more RNA motifs are discovered14 and as the interactions determining these motifs are better understood.
Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectra reveal two conformations for the RNA duplex, (5′GACGAGUGUCA3′)2, where the 3′ unpaired A increases duplex stability.15 The internal loop of the major conformation has two bulged-out U residues and two GG pairs with the G residues having syn glycosidic bonds, but it was not possible to deduce the entire structure of the internal loop. Here, we show that the two A residues in the internal loop are unpaired but stacked on each other and that their sugars are inverted. This defines a novel RNA structure that provides a new benchmark for programs predicting structure from sequence.
Determining all the structural features of the major conformation of the 5′GAGU3′ internal loop required assignment of at least four ambiguous nuclear Overhauser effects (NOEs) in (5′GACGAGUGUCA3′)2. This was accomplished by measuring spectra for the non-self-complementary duplexes, 5′GACGAGUGAGA3′/3′ACUGUGAGCUC5′, 5′GACGABrGUGAGA3′/3′ACUGUBrGAGCUC5′, and 5′GACGAMeGUGAGA3′/3′ACUGUMeGAGCUC5′, where BrG represents 8-Br-G and MeG represents 8-Me-G. As with (5′GACGAGUGUCA3′)2, the unmodified duplex has two conformations, but the 8-Br-G and 8-Me-G substitutions eliminate the minor species because the modified G residues are restricted to a syn conformation.15−19 Comparisons of one-dimensional (Figure 1) and two-dimensional spectra reveal that the 5′GAGU3′ internal loop of the major species has essentially identical conformations in all the duplexes studied. The average standard deviation of chemical shifts of equivalent loop protons in all six duplexes is 0.03 ppm, with a maximum of 0.09 ppm for G6 H1′ (Supporting Information). The non-self-complementary duplexes allowed assignment of NOEs to A5 that previously were ambiguous (Figure 2), e.g., A5 H2–G4* H1, A5 H8–G6 H1, A5 H1′–G6 H1, and A5 H8–G4* H8 (where an asterisk means the opposite strand). In the self-complementary duplexes, these could have been intra- or interstrand NOEs, allowing for 16 possible structures. Assignment allows definition of the positions of the A5 bases. In addition, a G4 H8–G8* H1 NOE was identified because an overlap was uncovered. This NOE confirms the GG pairing.
Figure 1.
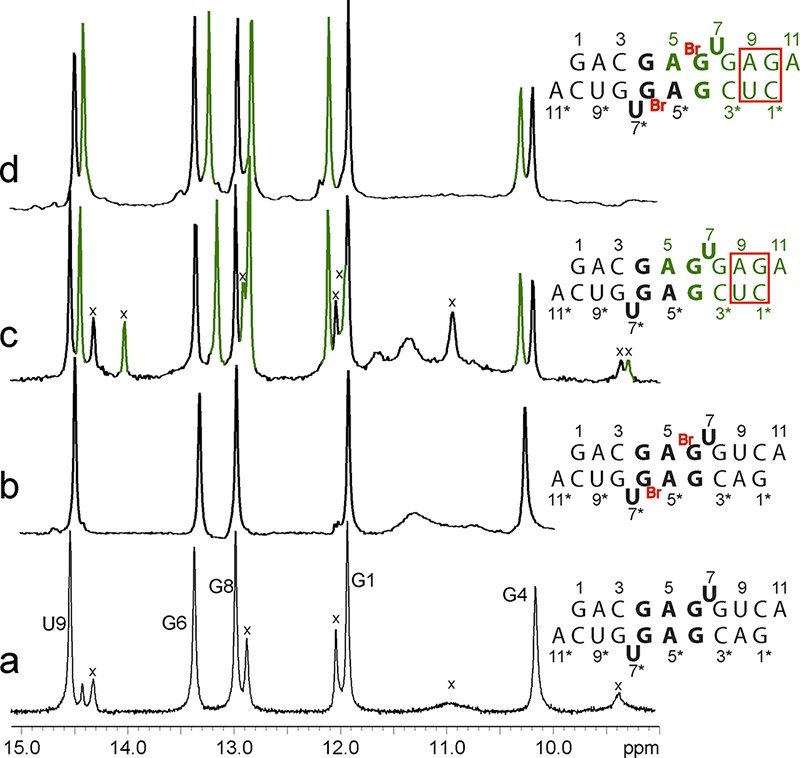
Imino proton spectra for RNA duplexes with the 5′GAGU/3′UGAG internal loop. Secondary structures of the major conformations are shown at the right. Peaks labeled with X are from the minor duplex conformation. The peak at 14.3 ppm in trace a is from a minor hairpin species. (a and b) Self-complementary sequences. (c and d) Non-self-complementary sequences. Black peaks and nucleotides are from the duplex half that is equivalent to the self-complementary duplex, and green peaks and nucleotides are from the duplex half that has a different sequence. (a and c) Natural nucleotides. (b and d) Duplexes with 8-Br-G6. Sample conditions: 80 mM NaCl, 0.05 mM EDTA, 20 mM sodium phosphate, pH 6, 1 °C.
Figure 2.
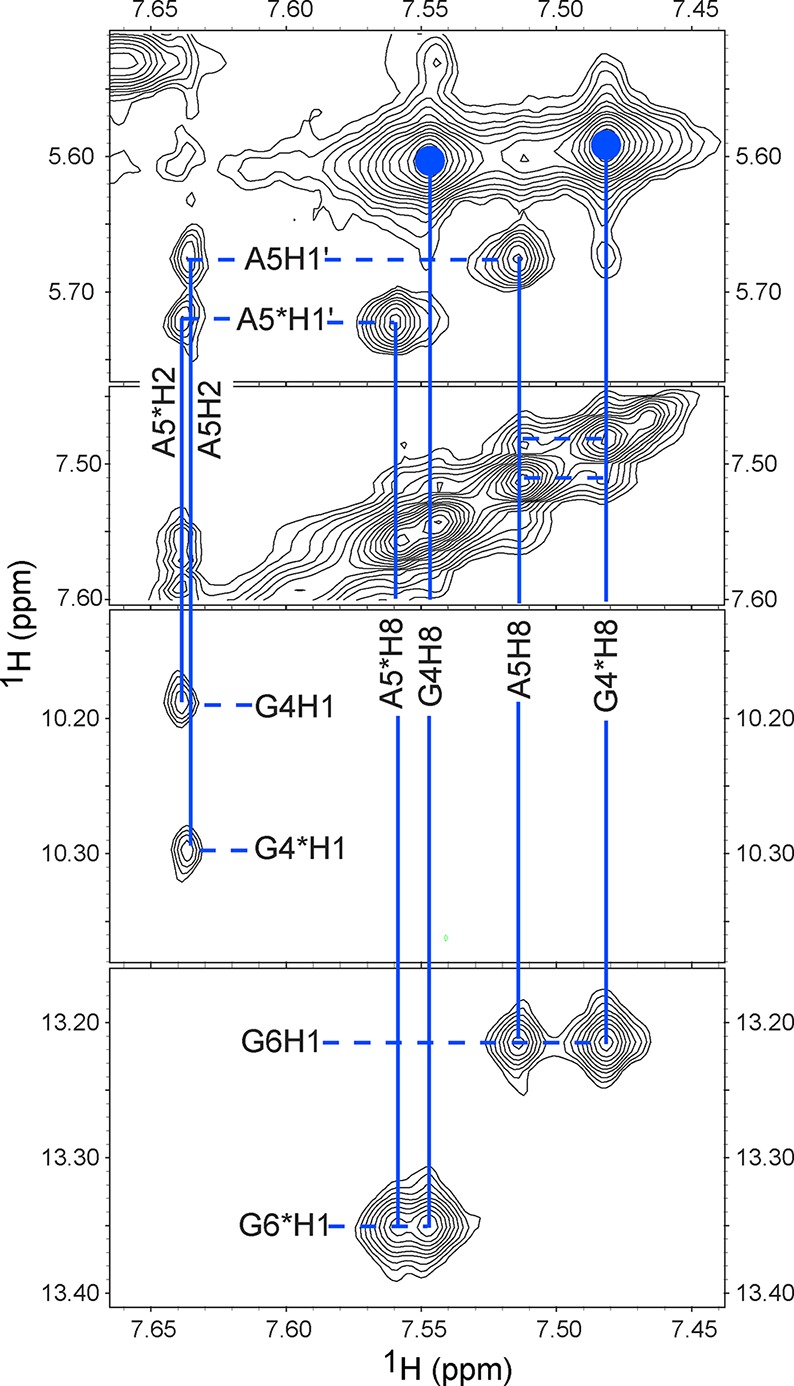
Watergate–NOESY spectrum of 5′GACGABrGUGAGA/3′ACUGUBrGAGCUC. Residues labeled with an asterisk are in the second strand. The regions displayed include cross-peaks for A5 and A5* aromatic protons. Two large cross-peaks labeled with blue filled circles are G4 H8–G4 H1′ and G4* H8–G4* H1′ cross-peaks and indicate that G4 and G4* are in the glycosidic syn conformation. Data were acquired at −2 °C with a 200 ms mixing time, except the diagonal panel, which was acquired at 1 °C with a 400 ms mixing time.
For modeling the structure, the majority of restraints were obtained from the 8-Br-G6-modified self-complementary duplex because the equilibrium between two conformations of the unmodified duplex can influence NOE volumes and make the spectra complex with many overlaps. Moreover, distance restraints derived for the modified self-complementary duplex and the major conformation of the unmodified duplex are in good agreement (Supporting Information). Six hundred rounds of simulated annealing in Generalized-Born implicit solvent with an initial temperature of 2000 K (protocol in the Supporting Information) with the NOE distance restraints and cross-strand hydrogen bond restraints for the GG pair produced only 27 structures that satisfied all NMR restraints. The root-mean-square deviation relative to the mean of 19 of these 27 structures subsequently refined without the GG hydrogen bond restraints was 0.89 Å, and a representative structure is shown in Figure 3. Structural statistics are given in the Supporting Information. The small fraction of structures consistent with NMR spectra may reflect approximations in the force field, effects of water, or the fact that the simulated annealing protocol does not easily allow transitions between conformations. No violations were found between the final structure and distances measured for the modified self-complementary duplex and the subset of distances measured for the major conformation of the unmodified duplex. Coordinates, restraints, and chemical shifts have been deposited in the Protein Data Bank as entry 2LX1.
Figure 3.
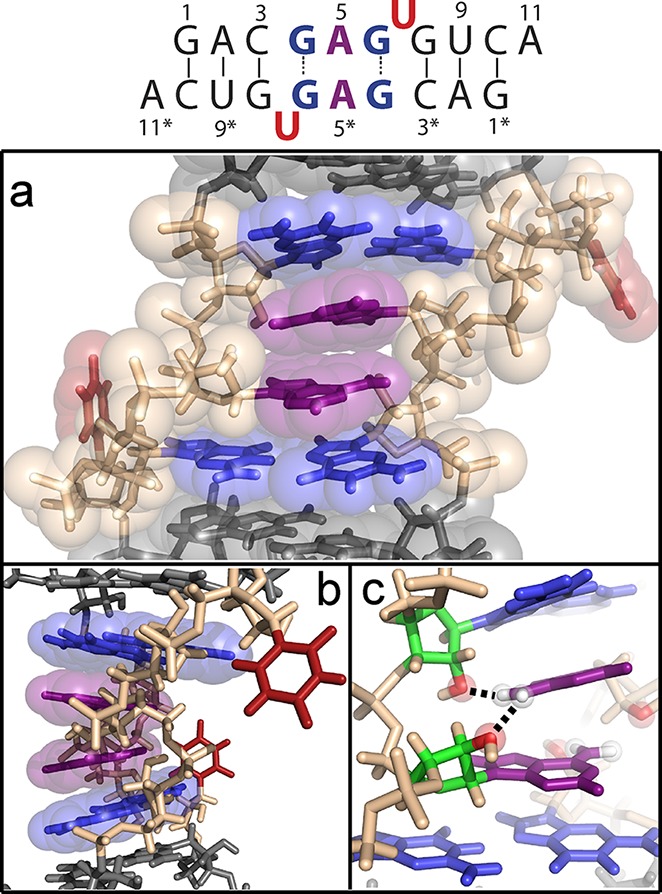
Major conformation of the 5′GAGU3′/3′UGAG5′ RNA internal loop. The secondary structure is shown at the top with residues colored as in the 3D model: (a) front view and (b) 90° rotation. (c) Potential stabilizing hydrogen bonds from A5 amino protons to 2′-oxygens of cross-strand G4* and A5*.
Notable features of the GAGU loop structure include (1) two U residues flipped out of the helix, (2) two GG* pairs with syn glycosidic bonds and G6–G4* trans Watson–Crick/Hoogsteen pairing, (3) C2′-endo sugar puckers for all loop residues (residues 4–7), (4) an A5/A5* stack within the helix, and (5) inverted A5 sugars. Key NOEs defining the inverted sugars include A5 H2′–G4 H3′ and A5 H4′–G6 H2′ NOEs (Supporting Information). Also, the chemical shift of A5 H5′ is ∼1.5 ppm upfield from typical A-form values,20 consistent with the position of that proton being directly below the ring of G6 as in the model. The relatively downfield chemical shift of G6 H2′ is consistent with that proton adjacent to the G6 base due to the syn conformation and C2′-endo sugar pucker.
The structure in Figure 3 is unique and was surprising for several reasons. The other five 5′XAGY3′ sequence symmetric internal loops,15,21 where XY is UG or any Watson–Crick pair, all have the expected canonical pairing between X and Y and the AG pairs have G imino to AN1 and GO6 to A amino hydrogen bonds (cis Watson–Crick/Watson–Crick conformation22). Inverted sugars are not common.23−26 Moreover, there are no obvious interactions driving the structure. The structure is consistent, however, with base stacking being sequence-dependent, as indicated by stacking of dangling ends on helices27,28 and by quantum mechanical calculations.29,30 The acceptable structures generated by simulated annealing contain hydrogen bonds between A5 amino protons and the 2′-oxygens of the cross-strand G4* and A5* that could be stabilizing interactions (Figure 3c). The inversion of the sugars apparently provides extra space to allow A5 to fit between G4* and A5* bases and positions G4* and A5* 2′-oxygens for hydrogen bonding. In addition, the models include intraresidue hydrogen bonds between a G4 amino proton and phosphate oxygen that may provide further stabilization. There is, however, no direct NMR evidence of any of these hydrogen bonds.
Methods for predicting 3D structures of RNA and an understanding of the interactions driving structure are at an early stage of development.8,31 The structure in Figure 3 presents a new benchmark for testing progress in both areas. Additionally, the structure provides a module with a unique arrangement of exposed chemical groups, such as A5 H2, A5 N1, G4 H1, and G4 NH2, that could be incorporated into designs for nucleic acid structures.32,33 The novel structure can be assured by including chemically modified nucleotides such as 8-Br-G, or it could serve as an environmentally sensitive switch. For example, small molecules could be designed or selected to shift the equilibrium to the minor or major structure of the GAGU internal loop. Identification of the minor conformation will facilitate such design and provide a known conformational equilibrium for testing force field predictions.
Supporting Information Available
Details of sample preparation, NMR spectroscopy, and simulated annealing protocol; a subset of proton chemical shifts of six duplexes studied; NMR restraints; and additional spectra. This material is available free of charge via the Internet at http://pubs.acs.org.
This work was supported by National Institutes of Health Grant GM22939 (to D.H.T.) and NSC Grants 2011/03/B/ST5/01098 and 2011/03/B/NZ1/00576 (to R.K.).
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Funding Statement
National Institutes of Health, United States
Supplementary Material
References
- Atkins J. F., Gesteland R. F., and Cech T. R. (2011) RNA Worlds from Life’s Origins to Diversity in Gene Regulation, Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Plainview, NY. [Google Scholar]
- (2012) Nature 489, 101–108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berman H. M.; Westbrook J.; Feng Z.; Gilliland G.; Bhat T. N.; Weissig H.; Shindyalov I. N.; Bourne P. E. (2000) Nucleic Acids Res. 28, 235–242. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summa C. M.; Levitt M. (2007) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 104, 3177–3182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley P.; Misura K. M.; Baker D. (2005) Science 309, 1868–1871. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Das R.; Baker D. (2008) Annu. Rev. Biochem. 77, 363–382. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiang L.; Althoff E. A.; Clemente F. R.; Doyle L.; Rothlisberger D.; Zanghellini A.; Gallaher J. L.; Betker J. L.; Tanaka F.; Barbas C. F. III; Hilvert D.; Houk K. N.; Stoddard B. L.; Baker D. (2008) Science 319, 1387–1391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cruz J. A.; Blanchet M. F.; Boniecki M.; Bujnicki J. M.; Chen S. J.; Cao S.; Das R.; Ding F.; Dokholyan N. V.; Flores S. C.; Huang L.; Lavender C. A.; Lisi V.; Major F.; Mikolajczak K.; Patel D. J.; Philips A.; Puton T.; SantaLucia J.; Sijenyi F.; Hermann T.; Rother K.; Rother M.; Serganov A.; Skorupski M.; Soltysinski T.; Sripakdeevong P.; Tuszynska I.; Weeks K. M.; Waldsich C.; Wildauer M.; Leontis N. B.; Westhof E. (2012) RNA 18, 610–625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Das R.; Baker D. (2007) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 104, 14664–14669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Das R.; Karanicolas J.; Baker D. (2010) Nat. Methods 7, 291–294. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parisien M.; Major F. (2008) Nature 452, 51–55. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernauer J.; Huang X.; Sim A. Y.; Levitt M. (2011) RNA 17, 1066–1075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sim A. Y.; Minary P.; Levitt M. (2012) Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 22, 273–278. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Das R. (2011) PLoS One 6, e20044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammond N. B.; Tolbert B. S.; Kierzek R.; Turner D. H.; Kennedy S. D. (2010) Biochemistry 49, 5817–5827. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tavale S. S.; Sobell H. M. (1970) J. Mol. Biol. 48, 109–123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michelson A. M.; Monny C.; Kapuler A. M. (1970) Biochim. Biophys. Acta 217, 7–17. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikehara M.; Uesugi S.; Yoshida K. (1972) Biochemistry 11, 830–836. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proctor D. J.; Kierzek E.; Kierzek R.; Bevilacqua P. C. (2003) J. Am. Chem. Soc. 125, 2390–2391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulrich E. L.; Akutsu H.; Doreleijers J. F.; Harano Y.; Ioannidis Y. E.; Lin J.; Livny M.; Mading S.; Maziuk D.; Miller Z.; Nakatani E.; Schulte C. F.; Tolmie D. E.; Kent Wenger R.; Yao H.; Markley J. L. (2008) Nucleic Acids Res. 36, D402–D408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu M.; SantaLucia J. Jr.; Turner D. H. (1997) Biochemistry 36, 4449–4460. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leontis N. B.; Stombaugh J.; Westhof E. (2002) Nucleic Acids Res. 30, 3497–3531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider B.; Moravek Z.; Berman H. M. (2004) Nucleic Acids Res. 32, 1666–1677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson J. S.; Schneider B.; Murray L. W.; Kapral G. J.; Immormino R. M.; Headd J. J.; Richardson D. C.; Ham D.; Hershkovits E.; Williams L. D.; Keating K. S.; Pyle A. M.; Micallef D.; Westbrook J.; Berman H. M. (2008) RNA 14, 465–481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Correll C. C.; Beneken J.; Plantinga M. J.; Lubbers M.; Chan Y. L. (2003) Nucleic Acids Res. 31, 6806–6818. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szewczak A. A.; Moore P. B. (1995) J. Mol. Biol. 247, 81–98. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burkard M. E.; Kierzek R.; Turner D. H. (1999) J. Mol. Biol. 290, 967–982. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner D. H. (2000) Conformational Changes. In Nucleic Acids: Structures, Properties and Functions (Bloomfield V. A., Crothers D. M., and Tinoco I. Jr., Eds.) University Science Press. [Google Scholar]
- Morgado C. A.; Svozil D.; Turner D. H.; Sponer J. (2012) Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 14, 12580–12591. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svozil D.; Hobza P.; Sponer J. (2010) J. Phys. Chem. B 114, 1191–1203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ditzler M. A.; Otyepka M.; Sponer J.; Walter N. G. (2010) Acc. Chem. Res. 43, 40–47. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeman N. C. (2010) Annu. Rev. Biochem. 79, 65–87. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaeger L.; Chworos A. (2006) Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 16, 531–543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.


