Fig. 6.
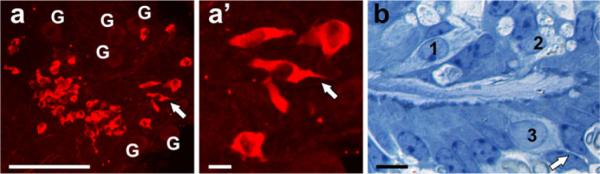
Deletion of Neurod1 results in transformation of cells, most likely sensory neurons into Myo7a positive “hair cells” (a). These cells are typically irregular or spindle-shaped and some of them display a more or less extended projection on the opposite part of the stereocilia/kinocilia, indicating a distinct polarity of the apex and the base of hair cells (arrows in a and a'). Most of these Myo7a-positive cells are found along ventricles formed inside the ganglia, into which they extend with their apical specializations. While some of these cells display multiple vesiculated structures near their base (1, 2 in b), others display a basal extension somewhat similar to the axon emanating from a neuron (3, arrow in b). G ganglion neurons. Bars (a) 100 μm, (a', b) 10 μm