Figure 1.
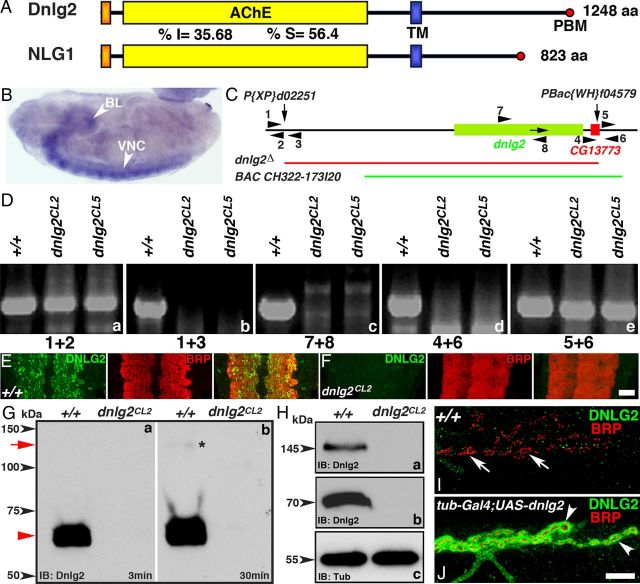
Generation of dnlg2 mutants. A, Protein domain structure of Drosophila Dnlg2 and human NLG1. Similar to human NLG1, Dnlg2 is composed of a signal peptide, an AChE-like domain and a TM domain followed by a PBM at the C terminus. The percentage amino acid identity (I) and similarity (S) between Dnlg2 and NLG1 in the AChE domains are indicated. B, In situ hybridization of wild-type embryo at stage 16 using a dnlg2-labeled antisense probe shows mRNA expression in the VNC (arrowhead) and brain lobes (BL, arrowhead). C, Genomic structure of dnlg2 and the flanking insertions, P{XP}d02251 in the 5′ end and PBac{WH}f04579 in the 3′ end. The arrows pointing down indicate the sites of insertion. The arrow in the dnlg2 locus shows the direction of transcription. The dnlg2-null mutant was generated using FRT-based recombination. The deleted genomic region is shown by the red line. A genomic BAC construct, P[acman]BAC CH322–173I20, spanning the region shown by the green line was used to rescue the deletion. D, PCR confirmation of the targeted deletion using different primer combinations. The PCR primer sets used are shown as numbers and arrowheads in C. E, F, VNC sections from third-instar larvae of wild-type (E) and dnlg2CL2 mutants (F) stained with anti-Dnlg2 (green) and anti-Brp (red) show expression of Dnlg2 in the synapse-rich regions of the VNC where Brp is expressed (E, merged image). Dnlg2 expression is absent in dnlg2 mutants (F). G, H, Immunoblot analysis of Dnlg2. Adult fly head extracts from wild-type (+/+) and dnlg2 mutants immunoblotted with anti-Dnlg2 antibodies. A shorter (G, a) and a longer (G, b) exposure time reveal the presence of a strong ∼70 kDa band in the wild-type lysate (red arrowhead). The blot with the longer exposure time shows the appearance of a faint ∼145 kDa band (G, b, red arrow, asterisk). Immunoblots with anti-Dnlg2 antibodies processed separately (H, a, b) detects the upper ∼145 kDa molecular weight (H, a, arrowhead) and the bottom ∼70 kDa band (H, b, arrowhead) in wild-type lysates that are absent in the dnlg2 lysates. For protein-loading control, the blot was probed with anti-α-tubulin (H, c, arrowhead). I, J, Third-instar larval NMJ from wild-type (I) and tubP-Gal4/UAS-dnlg2 (J) show expression of Dnlg2 (green) and Brp (red) at the NMJ synaptic boutons. Scale bars: (in F) E, F, 20 μm; (in J) I, J, 10 μm.