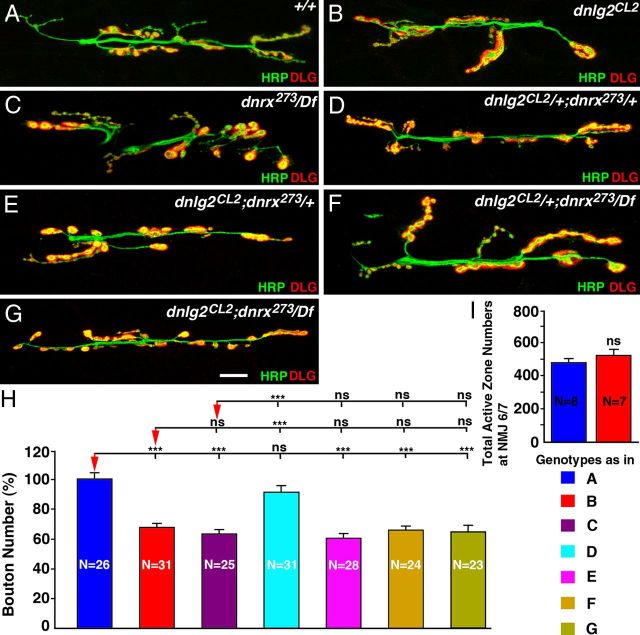
Figure 3.
dnlg2 and dnrx mutants display similar NMJ developmental defects. A–G, Confocal images of NMJ6/7 from abdominal segment 3 in third-instar larvae labeled with anti-HRP (green) and anti-DLG (red). Compared with control (w1118) (A), dnlg2 mutants (B), dnrx/Df mutants (C), dnlg2;dnrx+/− (E), dnlg2+/−;dnrx (F), and dnlg2;dnrx double homozygous (G) show fewer boutons. The NMJ morphology of transheterozygous dnlg2+/−;dnrx+/− (D) is unaffected. H, Quantification of total bouton number at NMJ6/7 adjusted to control bouton number. dnlg2;dnrx/Df single mutants, dnlg2;dnrx+/−, dnlg2+/−;dnrx/Df, and dnlg2;dnrx/Df double homozygous have ∼60–62% boutons compared with control. ***p < 0.001; **p < 0.01; *p < 0.05 (ANOVA, Tukey's post hoc test). Scale bar, 20 μm. I, Quantification of total AZ numbers at NMJ6/7. dnlg2 mutants have a comparable number of AZs with those observed at the wild-type NMJs (Student's t test). Genotypes in H are color coded and are same as in A–G.