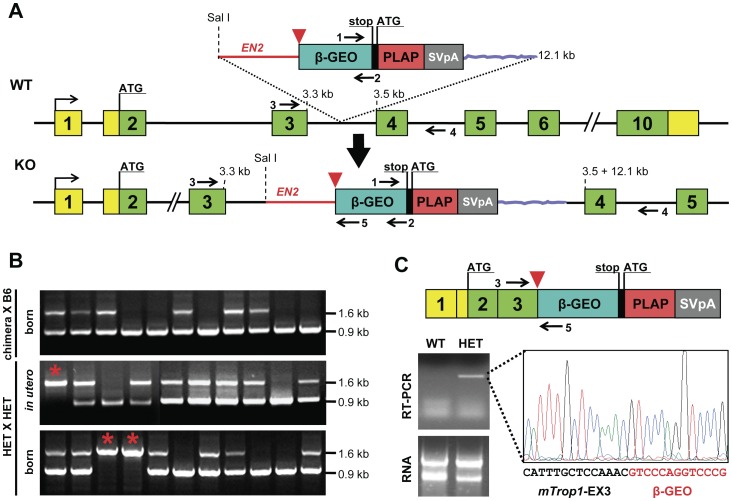
Figure 1. mTrop1 gene trapping.
(A) mTrop1 gene inactivation scheme for the RST412 and RST413 ES clones. The inactivating exonic cassette within the pGT1TMPF gene-trap vector (top) contains an ATG-less ORF of β-galactosidase fused to neomycin phosphotransferase (β–GEO, cyan), followed by an internal ribosome entry site (black) for placental alkaline phosphatase (PLAP) ORF (red); simian virus 40 transcription termination/polyadenylation signal (SVpA, gray); an intronic sequence from Engrailed2 (EN2) (red line) provides a strong splicing acceptor site (red arrowhead). The insertion brings the promoterless bicistronic β-GEO-PLAP-SVpA cassette in the third intron of WT mTrop1 (middle). Cassette insertion leads to a null (KO) mTrop1, by leading to the splicing of the mTrop1 exon 3 to the β-GEO cassette (bottom). Yellow boxes, mTrop1 untranslated exon sequences; green boxes, mTrop1 translated exons; arrows, PCR primer positions. (B) mTrop1 multiplex PCR genotyping. F1 litters from RST412 chimeric mouse males crossed to B6 females (top). Litters from HET crossings, in utero at E9.5 (middle) and after birth at day 1 (bottom). The 0.9 kb PCR fragment is from the WT allele (primers 3 and 4), the 1.6 kb PCR fragment is from the KO allele (primers 3 and 5). Homozygous KO mice were identified both in utero and in litters at birth (red stars). (C) The fusion transcript from the KO allele (top) is expressed in the intestine of HET mice, as revealed by RNA reverse transcription (RT)-PCR (bottom, left) and sequencing (bottom, right), with in-frame fusion between mTrop1 and β-GEO.