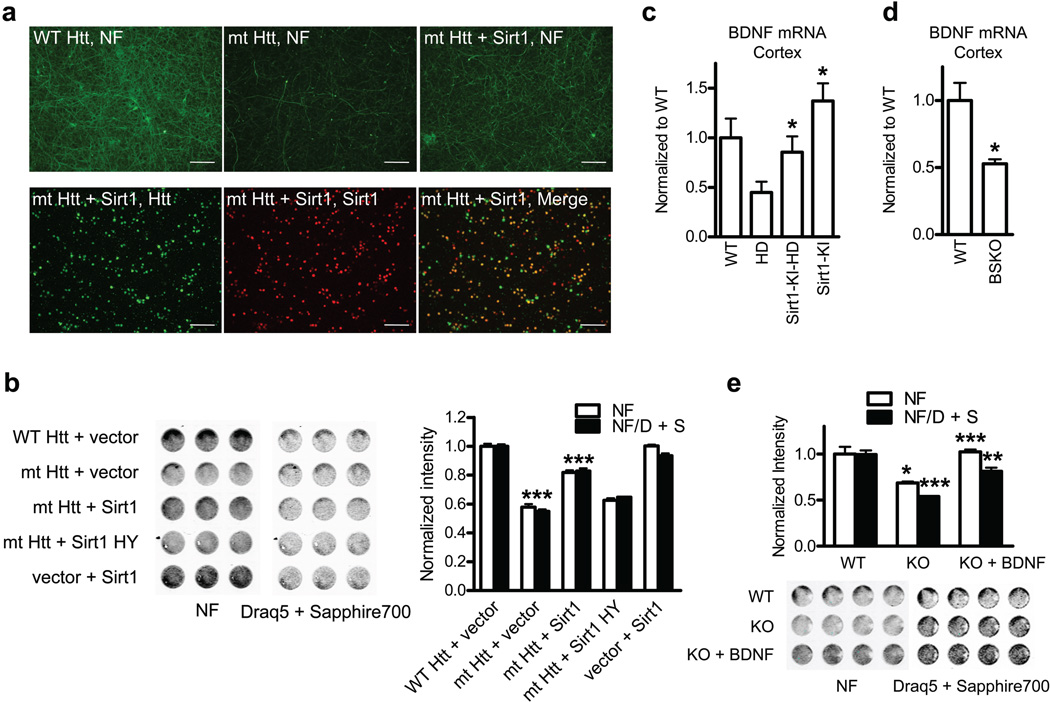
Figure 2. Deaceylase activity of Sirt1 protects cortical neurons from mutant HTT Toxicity.
(a) Upper panels: neurofilament (NF) staining in primary cortical neurons infected with indicated lentivirus. Lower panels: double staining of mt HTT- and Sirt1-infected neurons. Scale bar, 300 µm. (b) In-cell western (ICW) for NF and Draq5 + Sapphire 700 staining of cortical neurons infected with indicated lentivirus. *** P < 0.001 for mt HTT vs. WT HTT, *** P < 0.001 for mt HTT + Sirt1 vs. mt HTT. (c) BNDF mRNA levels in mouse cortex at 100 d of age. *P < 0.05 for HD vs Sirt1-KI-HD by ANOVA. * P < 0.05 for Sirt1-KI vs. WT by ANOVA (n=4 per group). (d) BDNF mRNA levels in mouse cortex at 3 months of age. n = 5 per group. *P < 0.05 by t-test. (e) Toxicity in primary cortical neurons from Sirt1 KO mice or WT littermates. * P < 0.05 for white bars, KO vs WT; *** P < 0.001 for black bars, KO vs WT; *** P < 0.001 for white bars, KO + BDNF vs KO; ** P < 0.01 for black bars, KO + BDNF vs KO by t-test.