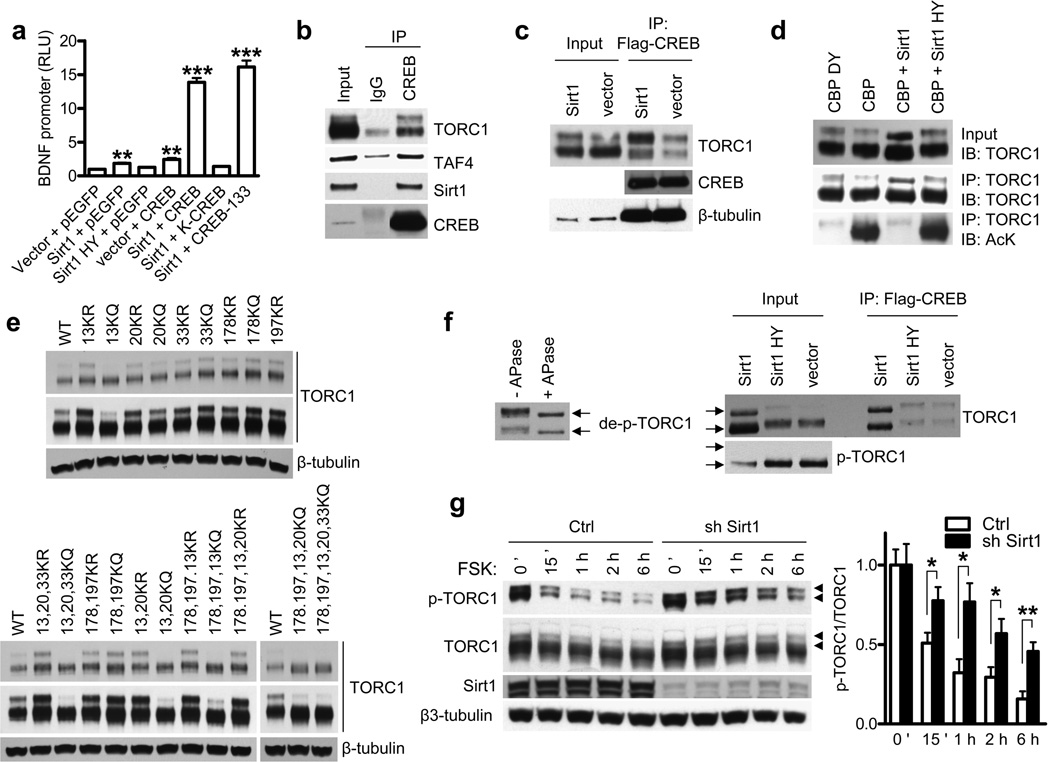
Figure 3. Sirt1 deacetylates and activates TORC1.
(a) BDNF promoter IV activity in N2a cells cotransfected with indicated plasmids at 24 h posttransfection. ** P < 0.01 vs. vector + pEGFP, ***P < 0.001 vs. vector + pEGFP by t-test. (b, c) Coimmunoprecipitations in N2a cells with indicated plasmids. (d) TORC1 immunoprecipitation and acetylation in N2a cells assessed by antibody to acetyl-lysine (AcK) (bottom panel). Western blots of TORC1 in input samples (top panel) and IP samples (middle panel). (e) Western blot of TORC1 KR or KQ mutants in N2a cells transfected with indicated TORC1 mutants. Long and short exposures are shown. (f) Left: western blot of TORC1 with or without in vitro treatment of alkaline phosphatase (APase). Right: Western blot of TORC1 and p-TORC1 and coimmunoprecipitation assay of CREB and TORC1 in N2a cells transfected with indicated plasmids. TORC1 position marked by arrows. (g) Dephosphorylation of p-TORC1 by forskolin (FSK) in the presence of Sirt1 knockdown in primary cortical neurons. Phospho-TORC1 marked with arrow heads. * P < 0.05 by t-test.