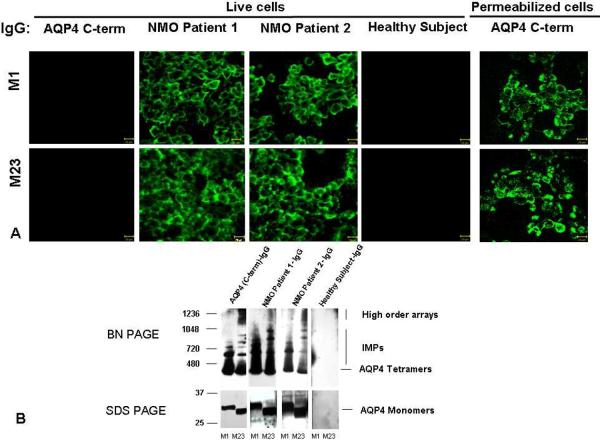
Figure 3.
A) Indirect immunofluorescence reveals disease-specific IgG binding to the extracellular domain of AQP4 in live HEK293 cells transfected with M1 or M23, as illustrated by sera of 2 NMOSD patients. Healthy (and disease control) serum IgG does not bind. By contrast, rabbit IgG specific for cytoplasmic AQP4 epitopes (C-terminal residues 249–323) binds only to permeabilized cells. B) Western blot analysis of M1 and M23 cell lysate proteins separated in “native” form by BN-PAGE and in denatured form by SDS PAGE. IgG in serum of 2 illustrative NMOSD patients binds to AQP4 tetramers and intramembranous particles (M1 and M23) and to high order arrays (M23), and to monomers of each AQP4 isoform. IgG in a representative healthy control human serum does not bind to any AQP4 protein. The control rabbit IgG is specific for AQP4 C-terminal residues. Note: M1 cells lack evidence of an M23 polypeptide product.