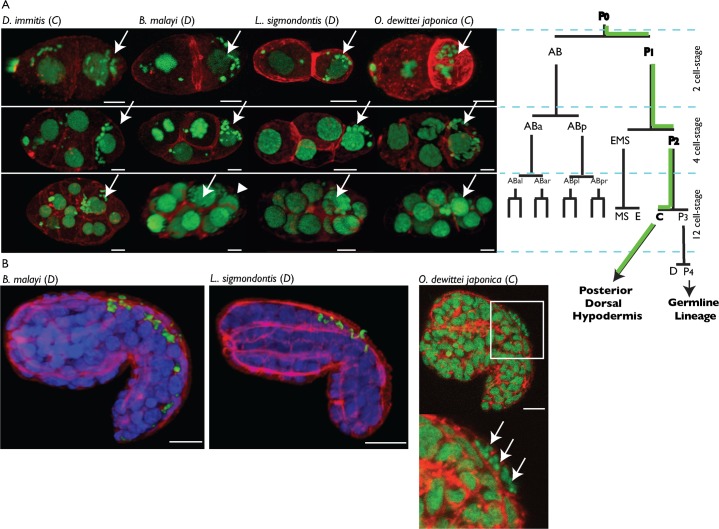
Fig. 1. Wolbachia supergroups C and D segregate into the C blastomere and its hypodermal progeny during filarial embryogenesis.
(A) Propidium iodide -green- and phalloidin -red- stainings of 2, 4 and 12-cell stage embryos. For sake of simplicity, the C. elegans lineage nomenclature was used to name the early blastomeres, based on the division pattern. The green path on the lineage tree shows the Wolbachia asymmetric segregation. On confocal images, arrows point to the blastomeres indicated in bold fonts on the lineage tree, and the arrowhead points to the P3 blastomere in the B. malayi 12-cell stage. In all species the AB lineage divides ahead of the posterior lineage. Anterior to the left. (B) Immunostainings of B. malayi and L. sigmondontis embryos in early elongation with an anti-WSP (green), PI -blue- and phalloidin -red-, cf. supplementary material Movies 3, 4. O. dewittei japonica is stained as in (A), arrows point to Wolbachia. Anterior to the right, dorsal part to the top. Scale bar = 5 µm.