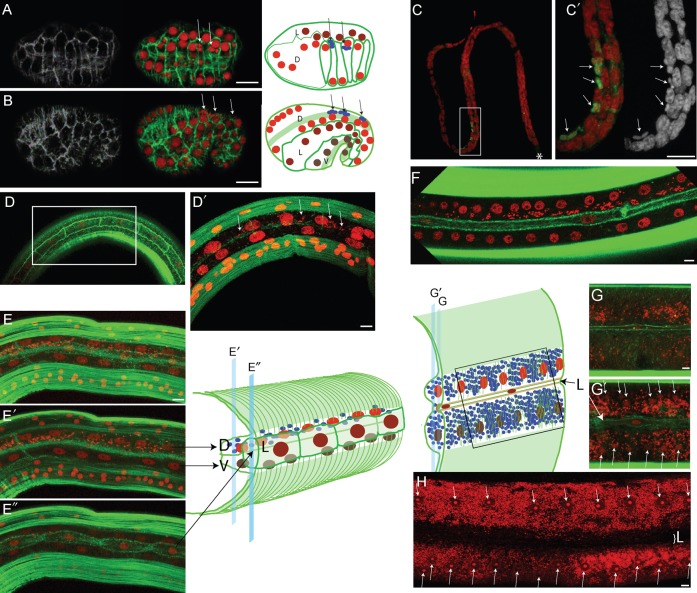
Fig. 2. Hypodermal cell fusion correlates with Wolbachia dispersion in B. malayi lateral chords.
All stages were stained with propidium iodide -red- and phalloidin -green-, except for (C,C′) where the anti-ftsZ is in green, and phalloidin was not used in (C,C′). (A) top view of the embryonic dorsal intercalation. (B) Lateral view of early elongation. In (A,B) arrows point to Wolbachia. In addition to cell membranes, the schematic drawing in (B) shows the underlying muscle precursors -green stripes-, and the Wolbachia -arrows pointing to blue foci-. D = dorsal hypodermis -red nuclei-; L = lateral hypodermis -burgundy nuclei-; V = ventral hypodermis -brown nuclei-. (C) Microfilaria stained with ftsZ, the star indicating the anterior. (C′) is a magnification of (C). (D,D′) Posterior lateral chord of a L3 at 3 dpi showing the hypodermal circumferential actin bundles reaching the unfused lateral hypodermal cells in (D), and (D′) the dorsal and ventral hypodermal syncytia underneath the lateral cells, with few Wolbachia in the dorsal syncytium (arrows). (E) Confocal merge of a posterior lateral chord in a L3 at 7 dpi, separating muscle quadrants. (E′) deep view showing the dorsal and ventral syncytia, with Wolbachia populating the dorsal hypodermis. (E″) surface view showing the yet unfused lateral hypodermis. (F) Merge of surface sections of a 30 dpi immature worm, showing the fused lateral syncytium, while the Wolbachia are still confined in the dorsal syncytium. (G,G′) section of an adult female lateral chord, showing the Wolbachia in the basal compartment (G), and a deeper view showing the ventral/dorsal syncytium chord with nuclei (arrows) surrounded by numerous Wolbachia (G′). The thin lateral hypodermal syncytium (“L”) does not fuse with the ventral/dorsal syncytium. Positions and depth of the G and G′ confocal images are indicated on the schematic drawing. (H) Adult female lateral chord, arrows point to the chord nuclei, “L” indicates the position of the lateral hypodermal syncytium. Note that in adult, the Wolbachia can occupy most of the lateral chord cytoplasm. Scale bar = 5 µm.