Figure 1.
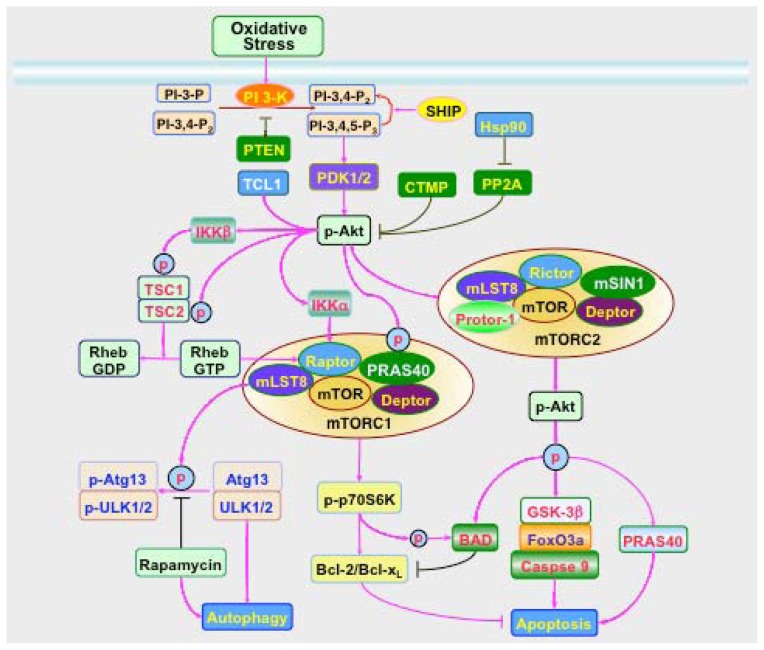
Signal transduction pathways of the PI 3-K, Akt, and mTOR cascade. During oxidative stress, multiple pathways are affected that involve PI 3-K, Akt, and mTOR that ultimately interface with programmed cell death pathways of apoptosis and autophagy. Activation of phosphoinositide 3 kinase (PI 3-K), such as by tropic factors that include erythropoietin can promote the production of phosphatidylinositide (3,4)-biphosphate (PI-3,4-P2) and phosphatidylinositide (3,4,5)-triphosphate (PI-3,4,5-P3) that recruits Akt to the plasma membrane. This recruitment activates phosphoinositide dependent kinase 1 (PDK1) and PDK2, leading to Akt phosphorylation. Akt activity can be blocked by the phosphatase and tensin homolog deleted from chromosome 10 (PTEN), SH2 domain-containing inositol phosphatase (SHIP), and carboxyl-terminal modulator protein (CTMP). Akt activity can be enhanced by the T cell leukemia/lymphoma 1 (TCL1) and 90 kDa heat shock protein (Hsp90) that can inhibit protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A). Akt can activate mTORC1 through phosphorylating TSC2 and disrupting the interaction between TSC2 and TSC1. Akt may also activate mTORC1 through I-kappaB kinase (IKK). IKKα associates with Raptor and IKKβ that can phosphorylate TSC1 and suppress TSC1 and its interaction with TSC2. In addition, Akt can directly phosphorylate proline rich Akt substrate 40 kDa (PRAS40) to reduce PRAS40 binding to regulatory associated protein of mTOR (Raptor) and thereby activate mTORC1. Upon activation, mTORC1 phosphorylates its downstream targets p70 ribosome S6 kinase (p70S6K) to phosphorylate pro-apoptotic protein BAD and increase the expression of Bcl-2/Bcl-xL which functions as an anti-apoptotic protein. mTORC1 activation also inhibits autophagic proteins autophagy related gene 13 (Atg13) and UNC-51 like kinase 1/2(ULK1/2) through phosphorylation to prevent autophagy. Rapamycin, an inhibitor of mTOR, can prevent this process and foster autophagy. mTOR signaling inhibits apoptosis though activation of Akt that inhibits “pro-apoptotic” proteins FoxO3a, glycogen synthase-3β (GSK-3β), BAD, and PRAS40.