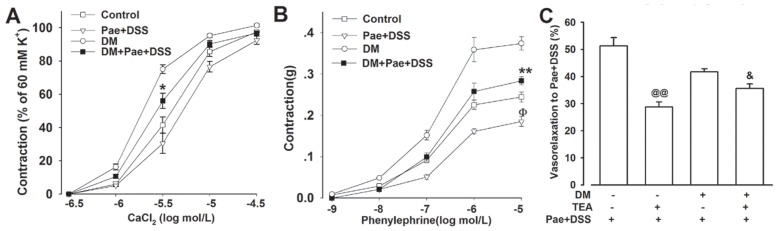
Figure 5.
Effects of Pae + DSS on calcium channels and K+ channel. (A) Rings without endothelium from control and diabetic rats were pre-incubated with or without Pae + DSS at 0.5 g/L for 10 min; the curves of CaCl2 in the Ca2+ free solution (containing 10 M to 4 M EGTA and 60 mM KCl) were inhibited by Pae + DSS (n = 6); (B) Pre-incubation with Pae + DSS at 0.5 g/L for 10 min significantly inhibited the vasocontraction of PE in Ca2+ free solution containing 10 M to 4 M EGTA of rings without endothelium from control and diabetic rats (n = 6); (C) Non-selective K+ channel blocker tetraethylammonium (TEA, 10 mmol/L) was pre-incubated with rings from control and diabetic rats for 10 min prior to stimulation with 1 μmol/L of PE. Pae + DSS (0.5 g/L) was added after the PE contraction reached a plateau. TEA significantly reduced Pae + DSS induced relaxation. **p < 0.01 and *p <0 .05 compared with the corresponding DM group, Φp < 0.05 compared with the corresponding control group, @@p < 0.05 compared with the control group treated with Pae + DSS, and &p < 0.05 compared with the corresponding DM group treated with Pae + DSS. Results are given as the mean ± SEM of three independent experiments.