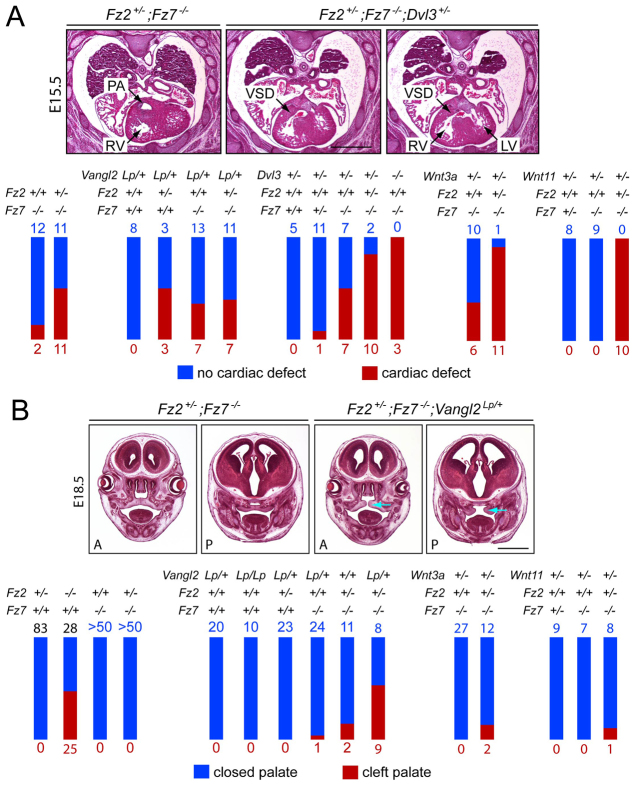
Fig. 3.
Tests for genetic interactions between Fz2, Fz7 and Vangl2, Dvl3, Wnt3a and Wnt11. (A) (Top) H&E-stained transverse paraffin sections showing cardiac defects in E15-18 mouse embryos. The vast majority were ventricular septal defects (VSDs), as seen upon comparing the normal cardiac anatomy of a Fz2+/−;Fz7−/− heart (left) with a pair of sections from a Fz2+/−;Fz7−/−;Dvl3+/− heart (right). PA, pulmonary artery; LV, left ventricle; RV, right ventricle. (Bottom) Summary of the numbers of embryos with the indicated genotypes and cardiac phenotypes. Each set of crosses is represented as a separate cluster of red and blue bars, with blue numbers and bars indicating embryos with no cardiac defect, and red numbers and bars indicating embryos with cardiac defects. Bar heights are normalized to the total number of embryos of the indicated genotype. (B) (Top) Palate closure defects in E18.5 embryos, as seen upon comparing the normal palate anatomy at anterior (A) and posterior (P) sites in an E18.5 Fz2+/−;Fz7−/− head (left pair of panels) with the cleft palate (blue arrows) of an E18.5 Fz2+/−;Fz7−/−;Vangl2Lp/+ head (right pair of panels). Most palates were scored intact after removing the lower jaw. Bottom, summary of genotypes and palate phenotypes as described for A. Scale bars: 1 mm.