Fig. 1.
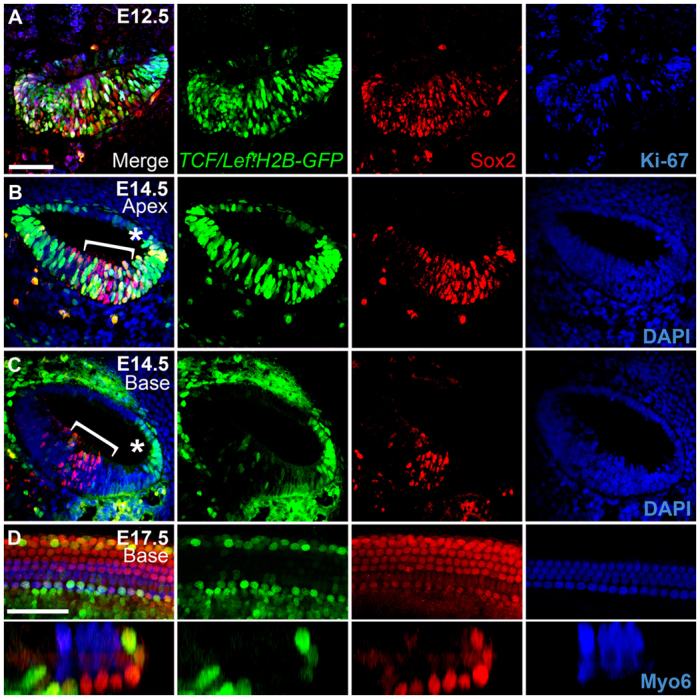
In vivo canonical Wnt/β-catenin reporter activity in the mouse developing cochlear duct. (A-C) Transverse sections through heterozygous E12.5 (A) and E14.5 (B,C) TCF/Lef:H2B-GFP reporter cochleae (medial is left, lateral is right). Merged views of GFP (green), Sox2 (red) and either Ki-67 or DAPI (blue) are shown on the left, with individual channels to the right. The apical (B) and basal (C) turns from the same E14.5 section are shown (a low-magnification image of this section is shown in supplementary material Fig. S3). Asterisk indicates the stria vascularis; brackets indicate the Sox2-positive domain. (D) High-magnification lumenal surface view (top) and z-section (bottom) of an E17.5 TCF/Lef:H2B-GFP reporter cochlea; colors are the same as above, except that hair cells (HCs) are labeled for myosin 6 (Myo6, blue). Note that for E14.5 confocal images, settings were calibrated to the brightest apical region in the sample and these settings were used for the high-magnification imaging of the basal region; thus, levels in the base appear much weaker than in the E17.5 sample, which was calibrated separately. Scale bars: 50 μm.
