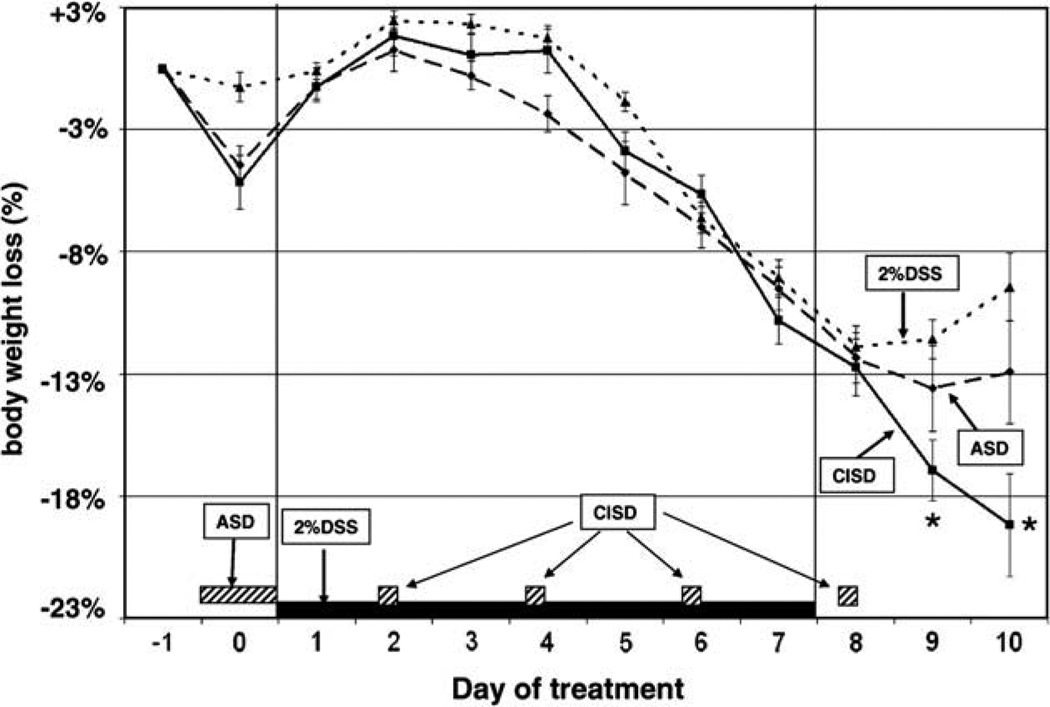
Fig. 1.
Effect of acute and chronic intermittent sleep deprivation on weight loss in 2% DDS-induced colitis mice. Weight loss relative to the animal’s base weight before induction of colitis was measured daily as a biomarker for colitis. Acute sleep deprivation (ASD) was achieved by forced wheel walking for 24 h prior to the administration of 2% DSS (as indicated by the dotted box). Chronic intermittent sleep deprivation (CISD) was a combination of an acute 24 h period of sleep deprivation followed by 6 h of forced activity in the wheel every other day after day 1 (as indicated by the dashed boxes on the x-axis). ASD or CISD increased weight loss caused by 2% DSS. Animals in the ASD & CISD groups received 7 days of 2% DSS treatment in their drinking water. There was a significant difference in weight loss in the CISD groups compared with controls (2% DSS alone) during the recovery period (days 9 and 10). Data are expressed as mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05 compared with the no sleep deprivation control group.