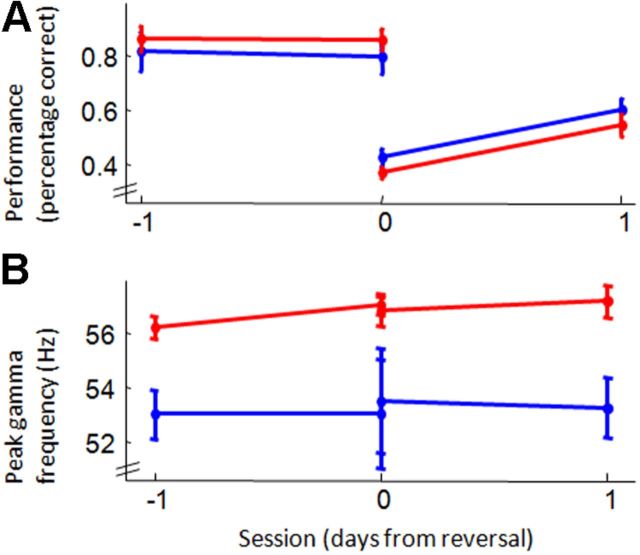
Figure 2.
Task performance and gamma frequency before and after task switch. A, Performance on the visual version of the three-choice, two-cue task (y-axis) across sessions (x-axis). Performance of both aged (blue) and young (red) adult rats exceeded 80% on the session and the trials before a switch to rewarded auditory cues. After a switch from rewarded auditory to rewarded visual cues, performance dropped and recovered over subsequent days. Performance on the auditory task followed these same patterns, though aged rats performed more poorly than did young adults both before and after cue-reward reversals (data not shown). B, Mean peak gamma frequencies for the same sessions and trials shown in A. Gamma frequency did not significantly change for either age group across sessions and was consistently lower in the aged rats.