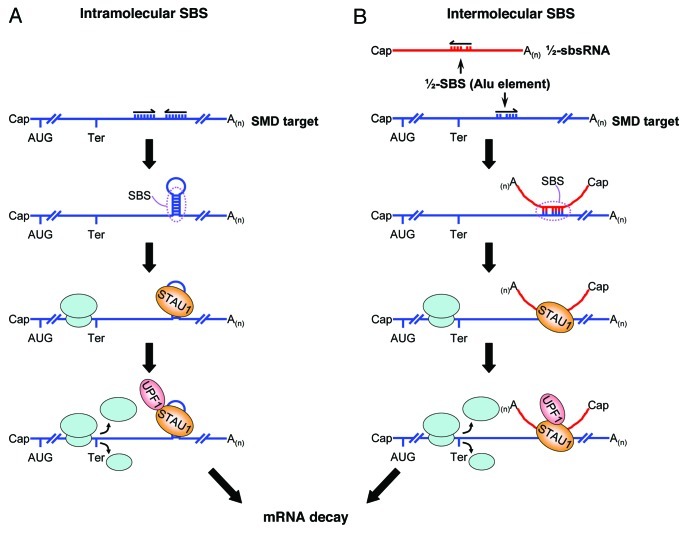
Figure 1. Two mechanisms of SBS formation. An SBS that triggers SMD can be formed by (A) intramolecular base pairing within an mRNA 3′UTR or (B) intermolecular base-pairing between a ½-SBS within an mRNA 3′UTR and a partially complementary ½-SBS Alu element within a lncRNA (½-sbs RNA). Those ½-SBSs characterized to date derive from Alu elements. While the features of either intramolecular or intermolecular SBSs have yet to be determined, intermolecular SBSs, which have been found to vary in size from 86 to 264 base pairs (but may have sizes outside of this range), contain multiple bulges, each of which does not exceed two nucleotides. When translation terminates sufficiently upstream of an SBS, so the terminating ribosome does not displace SBS-bound STAU1, the interaction of SBS-bound STAU1 with UPF1 triggers SMD. While not shown, it is conceivable that more than one STAU1 molecule binds to a given SBS in a way that depends on SBS length.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.