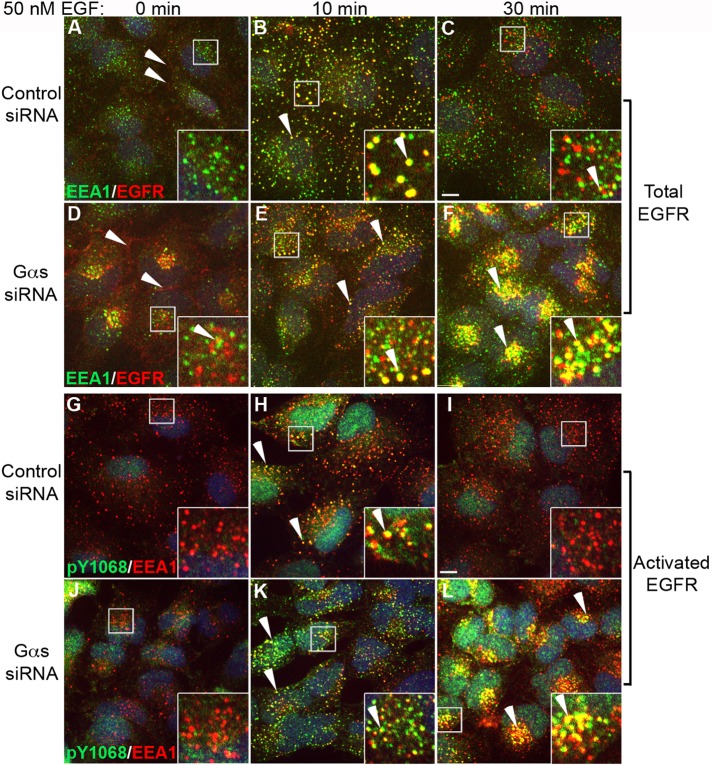
FIGURE 2:
Gαs depletion prolongs and enhances EGFR signaling from EEA1 endosomes. (A–F) Gαs-depleted and control HeLa cells were serum starved, stimulated with 50 nM EGF for 0, 10, or 30 min, stained for total EGFR (red) and EEA1 (green), and analyzed as in Figure 1. In controls (A) before EGF stimulation (0 min) EGFR is found at the PM (red, arrowheads) and occasionally in intracellular vesicles that mostly do not colocalize with EEA1 (green, inset). At 10 min after stimulation (B) EGFR localizes to EEA1 early endosomes (yellow, arrowheads), and by 30 min (C) relatively few EGFR remain in EEA1 endosomes. In Gαs-depleted cells, before EGF stimulation (D) EGFRs are also concentrated near the PM (red, arrowhead) and in intracellular vesicles, which sometimes colocalize with EEA1 (yellow, inset). At 10 min after stimulation (E), colocalization with EEA1 in early endosomes is increased; by 30 min (F) there is a striking accumulation of EGFR in juxtanuclear clusters of EEA1 endosomes in Gαs-depleted cells (yellow, F), whereas little EGFR remains in controls (C). (G–L) Gαs-depleted HeLa cells and controls were treated as in A–F and stained for activated (phosphorylated) pY1068-EGFR (green) and EEA1 (red). After serum starvation (0 min), little pY1068 staining for activated receptors is observed at the PM or at EEA1 endosomes in either control (G) or Gαs-depleted (J) cells. At 10 min after stimulation activated EGFRs are associated with EEA1 endosomes in both control (H) and Gαs-depleted (K) cells (yellow, arrowheads). By 30 min, activated EGFRs are barely detectable in EEA1 endosomes (red) in controls (I), whereas there is a striking accumulation of activated EGFR in juxtanuclear clusters of EEA1 endosomes (yellow, arrowheads) in Gαs depleted cells (L). Bar, 10 μm. Insets, 3× enlargement of boxed regions.