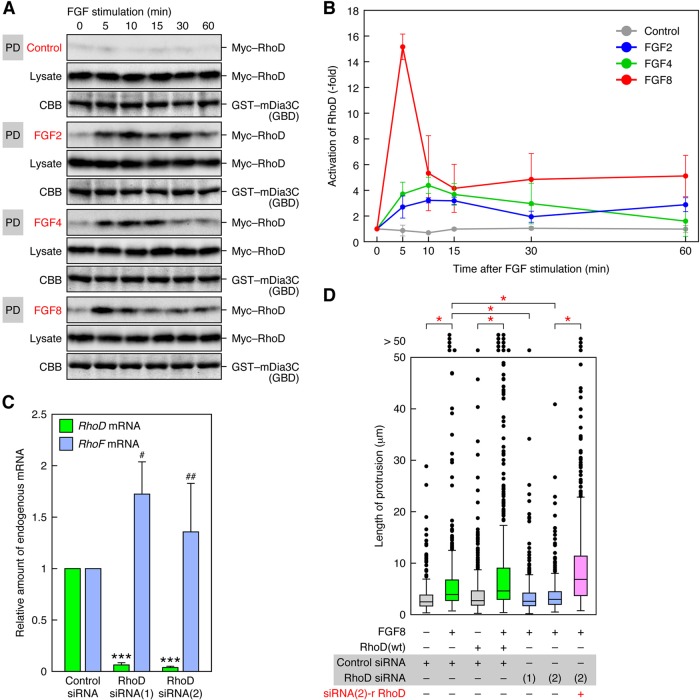
FIGURE 4:
RhoD is activated by FGF stimulation and required for FGF-induced protrusion formation. (A) Activation of RhoD by FGF stimulation. Activation of RhoD was analyzed by a pulldown assay with GST–mDia3C(GBD) and lysates of Myc–RhoD(wt)-transfected 10T1/2 cells stimulated with FGF2/4/8. Myc–RhoD was detected by immunoblotting with the anti-Myc mAb. (B) The degree of RhoD activation by FGF stimulation in the analysis of (A). The values are mean ± SD of three independent experiments. (C) Specific suppression of RhoD expression by RhoD siRNAs. The 10T1/2 cells were transfected with RhoD Stealth siRNA(1) or (2). The levels of endogenous RhoD and RhoF mRNAs were analyzed 48 h after the transfection by real-time PCR. The values are normalized with β-actin mRNA levels. ***, p < 0.001; #, p = 0.095; ##, p = 0.36 (not significant) by t test compared with control siRNA transfection. (D) Requirement of RhoD for FGF8-induced protrusion formation. The 10T1/2 cells were first transfected with Stealth siRNAs and 48 h later with EGFP–RhoD(wt) or siRNA(2)-resistant EGFP–RhoD. The cells were stimulated for ∼60 min with FGF8 48 h after the RhoD transfection, and the protrusion length was analyzed. n > 390. *, p < 0.0001 by t test.