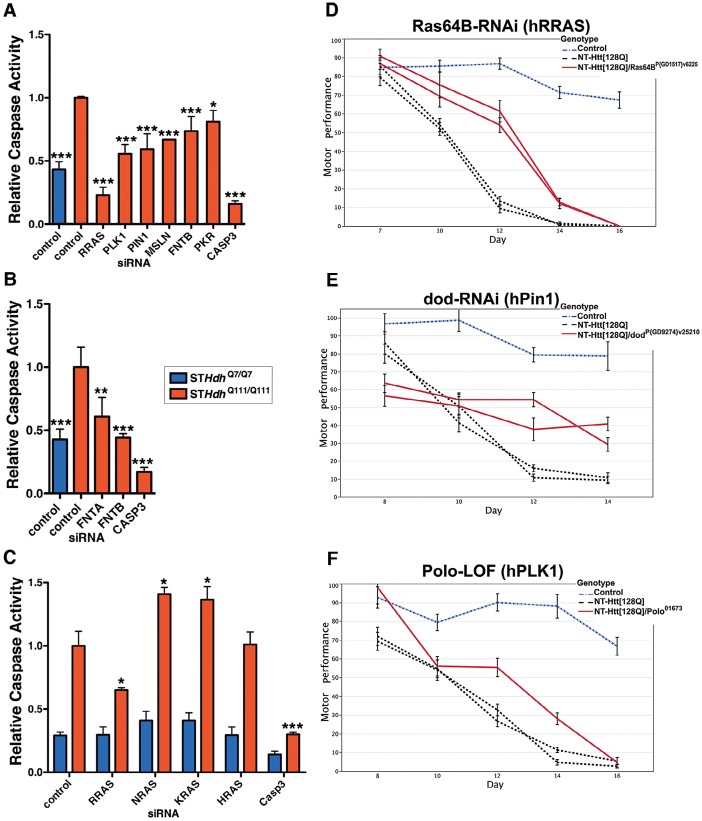
Figure 4. Suppression of Htt Toxicity by Knock-Down of RRAS Signaling Is Conserved across HD Models.
(A) Knockdown of Ras signaling components in STHdh Q111/Q111 cells (n = 3). See Figure S4A for data using individual siRNAs from deconvoluted pools. (B) siRNA targeting of subunits of the farnesyltransferase enzyme in STHdh Q111/Q111 cells (n = 3). (C) Toxicity suppression is specific to RRAS knockdown among Ras family members tested (n = 3). *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, ANOVA with Tukey's Multiple Comparison Test. Figure S4B shows confirmation of knockdown by western blot. (D–F) Loss-of-function in Ras signaling components Ras64B (RRAS), dod (PIN1), and polo (PLK1) suppress motor performance defects in Drosophila melanogaster caused by expression of mutant Htt (See Figure 3C; additional results are also presented in Figure S5). Error bars represent s.e.m.