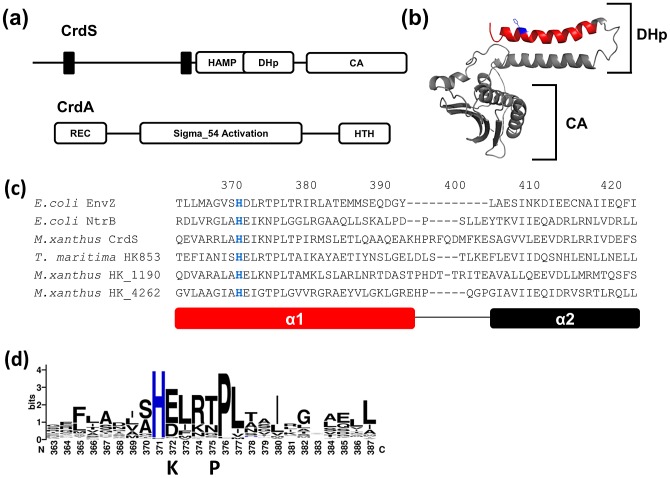
Figure 2. Sequence Analysis of CrdS and HisKA Domains.
(A) Domain organization of the histidine kinase, CrdS, and its cognate response regulator, CrdA. CrdS is composed of a predicted N-terminal periplasmic sensing domain followed by HAMP, DHp and CA domains. CrdA is a σ54-dependent transcription factor regulating developmental gene expression. (B) Predicted structure of the soluble portion of CrdS after threading onto the structure of T. maritima HK853. The DHp domain (spanning α1 and α2 helices) and CA domain are indicated by brackets. The α1 helix of CrdS (red) containing the conserved phosphorylatable histidine (blue) was subjected to mutagenesis. (C) Sequence alignment of CrdS with other HisKA DHp domains spanning the α1 (red) and α2 helices. Residues are numbered relative to their position in CrdS. (D) Sequence conservation across α1 helices of the 100 most diverse HisKA DHp domains. “K” and “P” indicate residues required exclusively for kinase and phosphatase activity, respectively.