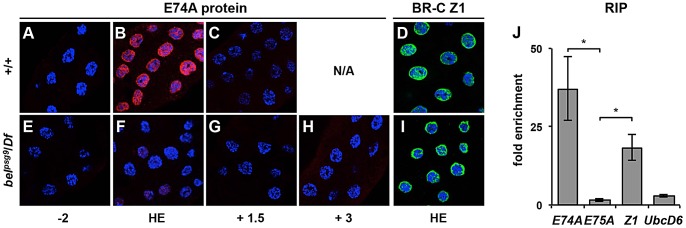
Figure 4. Belle directly regulates E74A mRNA translation.
(A–I) Salivary glands dissected from animals staged relative to head eversion and stained with antibodies directed to E74A protein shown in red (A–C and E–H) or to BROAD Z1 protein in green (D, I) with DAPI costained nuclei in blue. (A–C) In control salivary glands, E74A protein is detected at head eversion (HE)(B), but not 2 hours before HE (A) or 1.5 hours AHE (C) (N/A: control glands are too fragile to dissect after +1.5 AHE). (E–H) In belpsg9 mutant salivary glands, E74A protein is barely detectable at stages before, during or after head eversion. (D–I) In contrast, both control and belpsg9 mutant salivary glands express BROAD Z1 protein at head eversion. (J) Ribonucleoprotein (RNP) immunoprecipitation (RIP) experiments with BEL-GFP fusion protein, followed by qPCR analysis for target mRNAs. E74A and BR-C Z1 transcripts showed significant (37-fold and 18-fold, respectively) enrichment in BEL-GFP containing RNP complexes, while E75A and UbcD6 transcripts did not show significant enrichment. Data represent average qPCR results from three independent RIP experiments; asterisks indicate p-values <0.05. HE: head eversion, Z1: BR-C Z1.