Figure 6. Expression of E74A protein–dependent ecdysone late-response genes is disrupted in belle glands.
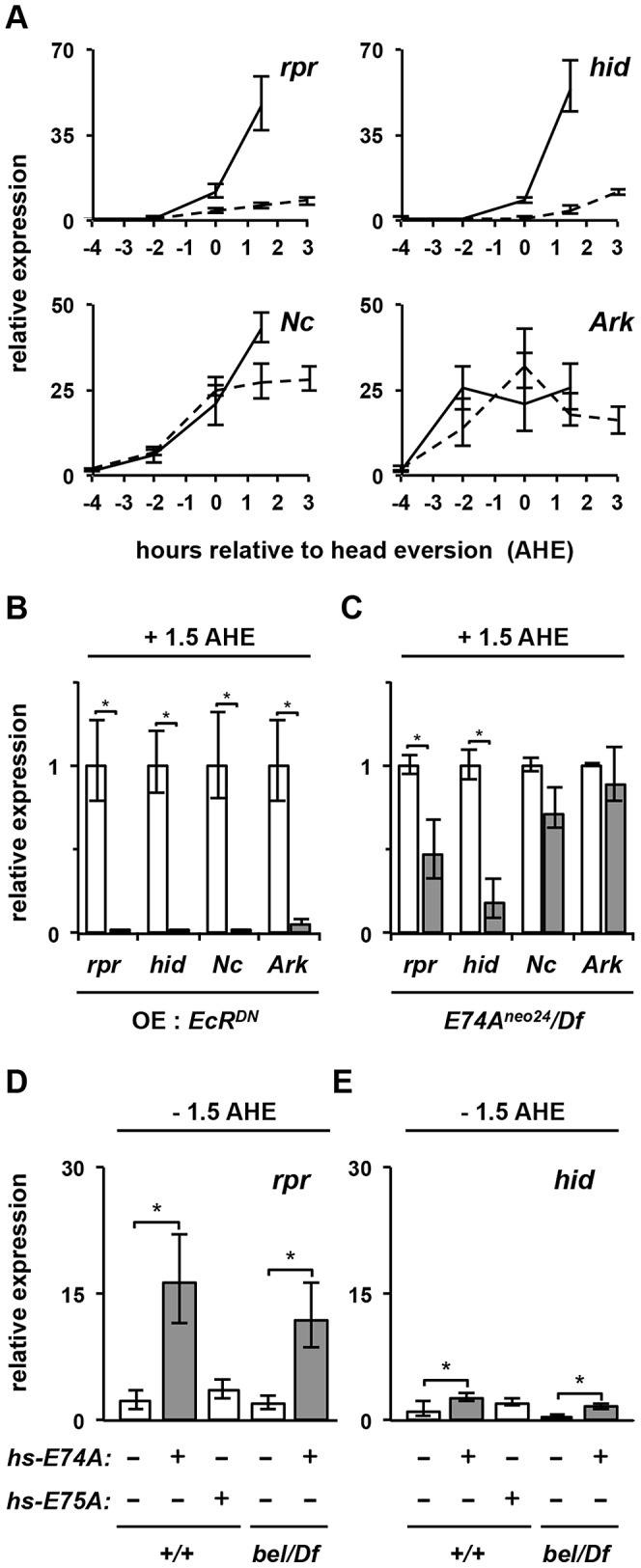
(A) belpsg9 is required for ecdysone-induced expression of death activators rpr and hid, but not Nc and Ark. x-axis plots timecourse of salivary glands dissected from control (solid lines) and belpsg9/Df (dashed lines) animals staged relative to head eversion (AHE) (salivary glands cannot be recovered from control animals after +1.5 AHE). (B) Ectopic expression of dominant negative ecdysone receptor prior to the prepupal pulse of ecdysone blocks expression of death regulators rpr, hid, Nc, and Ark in salivary glands. Control (white bars) and OE: EcRDN (UAS-GAL4/UAS-EcRF645A; hs-GAL4/+) (gray bars) preupupae were heat-shocked four hours before head eversion (−4 AHE), re-staged at head eversion and salivary glands were dissected at +1.5 AHE, a stage when these death genes are maximally expressed. (C) E74A is required for ecdysone-induced expression of death activators rpr and hid, but not Nc and Ark. Relative expression of death regulators in salivary glands dissected from control (white bars) or E74Aneo24/Df mutant (gray bars) animals. (D–E) Precocious expression of E74A protein (gray bars) is sufficient to significantly induce expression of rpr (D) and hid (E) in salivary glands (experimental paradigm as Figure 5A). (D) Ectopic expression of E74A protein in control (second bar from left) and belpsg9 mutant (fifth bar from left) animals show significant induction of rpr. In contrast, ectopic expression of E75A protein (third bar from left) does not show any effect. (E) Similar experiments measuring hid expression show minor but statistically significant changes. y-axis plots relative expression, normalized to rp49. Expression ratios in 6D and 6E calculated relative to −4 AHE control samples to show induction in response to the prepupal pulse of ecdysone. All samples are in triplicate; asterisks indicate p-values <0.05. bel/Df: belpsg9/Df. AHE: after head eversion.
