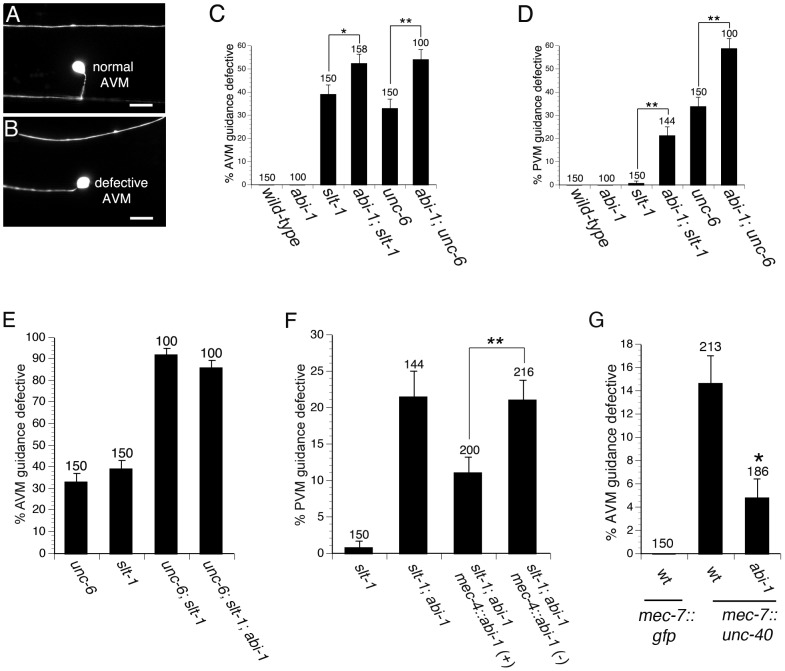
Figure 2. ABI-1 is involved in both UNC-6 and SLT-1 signaling pathways.
(A) Example of AVM neuron with normal ventral guidance. (B) Example of AVM neuron with defective ventral guidance. (C–D) Genetic interactions between unc-6 and abi-1 as well as between slt-1 and abi-1 in the AVM (C) and PVM (D), indicate that ABI-1 functions in both the UNC-6 and SLT-1 signaling pathways. (E) Loss of abi-1 function does not enhance defects in the unc-6; slt-1 mutant background. (F) ABI-1 functions cell autonomously to mediate axon guidance. A mec-4::abi-1 transgene suppresses PVM ventral axon guidance defects in slt-1; abi-1 double mutants. mec-4::abi-1(−) represents animals that have lost the mec-4::abi-1 transgene during mitosis. These animals serve as controls and were scored simultaneously on the same slides as the mec-4::abi-1(+) animals, which carry the transgene. Data was combined from 2 independently derived transgenic lines, cueEx1 and cueEx2, which showed similar results. (G) The abi-1(tm494) loss of function mutation suppresses guidance defects in AVM neurons overexpressing UNC-40. Scale bars are 5 µM. Error bars represent standard error of the proportion. Brackets indicate statistically significant difference, Z test for proportions (*p<0.05, **p<0.005). The AVM axon was visualized with the zdIs5 transgene (mec-4::gfp). Scale bars are 10 µM. Alleles used were unc-6(ev400) null, slt-1(eh15) null, and abi-1(tm494) loss of function.