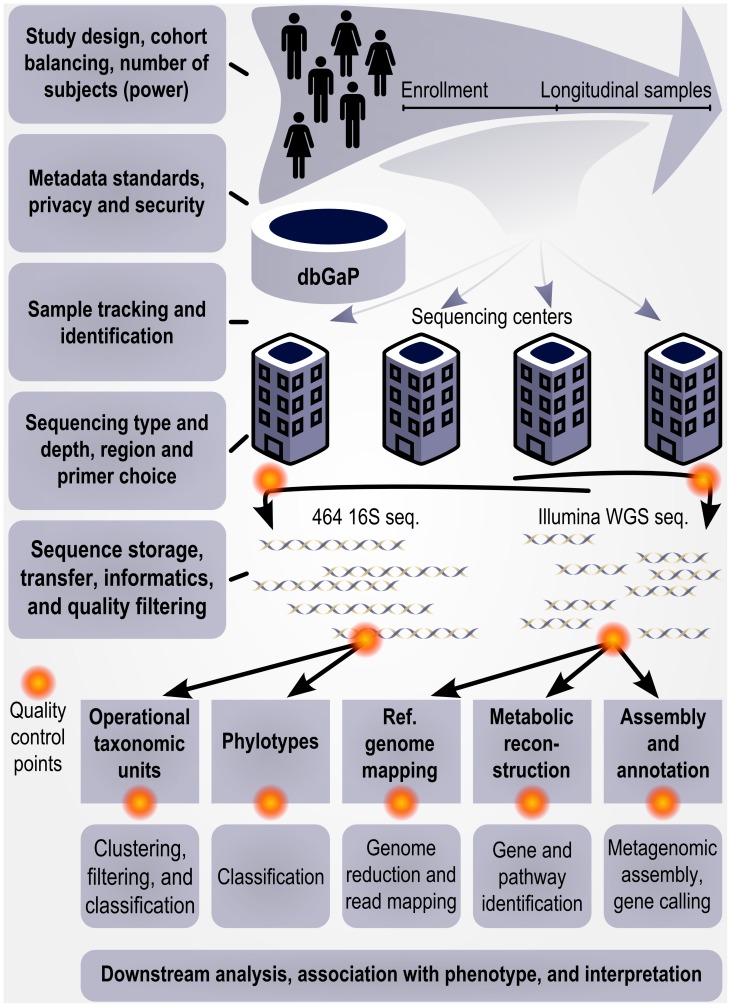
Figure 1. Bioinformatics in the HMP as a model for further studies of the human microbiome.
Important computational considerations throughout the design, implementation, and analysis of a large human microbiome study such as the HMP; for details of the HMP's specific computational protocols, see [7], [42]. In the HMP, study design considerations included cohort balancing for gender and geographic location and recruitment of 300 individuals for adequate power. Subject metadata were protected and distributed through dbGaP [11], and up to three longitudinal samples were drawn from the microbiomes of 18 body habitats. These were tracked and sequenced at up to four distinct centers, including >5,000 16S rRNA gene datasets using 454 reads from the V1–3 and V3–5 hypervariable regions and >700 Illumina whole-genome shotgun datasets totaling over 8 Tbp of sequence. Quality control of sequences and datasets was performed at multiple points throughout data generation. Computational pipelines were developed and documented for each sequence data product as well as downstream analyses, with full results and protocols available at the HMP Data Analysis and Coordinating Center (http://hmpdacc.org).