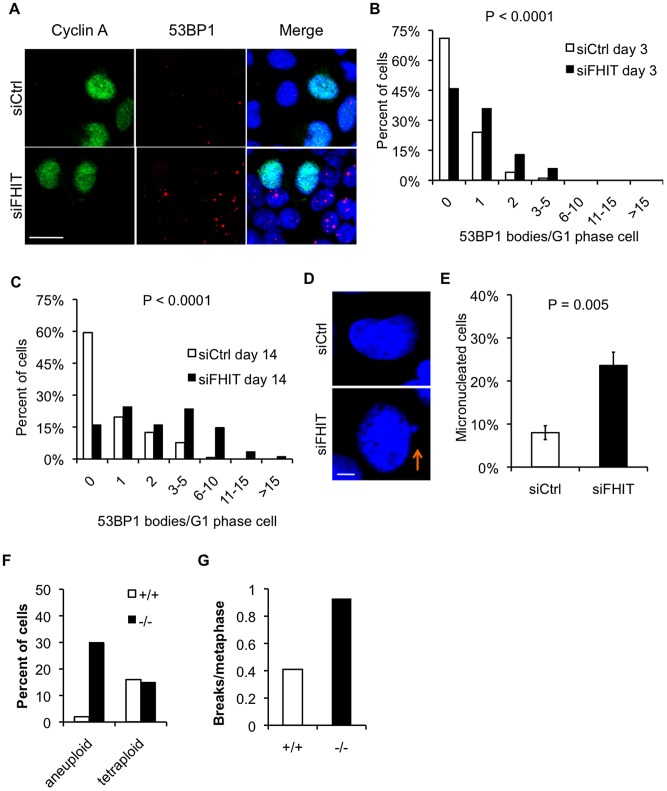
Figure 6. Loss of Fhit causes replication stress-induced chromosomal instability.
(A) Cyclin A and 53BP1 immunofluorescence after Fhit knockdown in HEK293 cells. Representative images are shown; bars, 20 µm. (B and C) Histograms of 53BP1 nuclear bodies/G1 phase cell 3 days following siRNA transfection (B) or 14 days after siRNA transfection with fresh siRNAs transfected every 4 days (C). G1 phase cells were defined as cells negative for Cyclin A staining. Mann-Whitney rank sum test was used to determine P-values. (D) Representative images of DAPI-stained nuclei in siCtrl or siFHIT cells. Arrow marks a micronucleus; bars, 5 µm. (E) Quantification of micronucleated cells 3 days after siRNA transfections. Bar graphs represent the means, and error bars mark the standard deviations. P-value determined using a 2-sided T-test. (F) Percentage of aneuploid or tetraploid kidney cells established from Fhit+/+ or Fhit−/− mouse kidney epithelial cells. Cells were sub-cultured 8 times and metaphase chromosomes were prepared and counted (n = 37 for Fhit+/+; n = 40 for Fhit−/− metaphases). (G) Quantification of the number of breaks/metaphase for the mouse kidney cells described in (F).