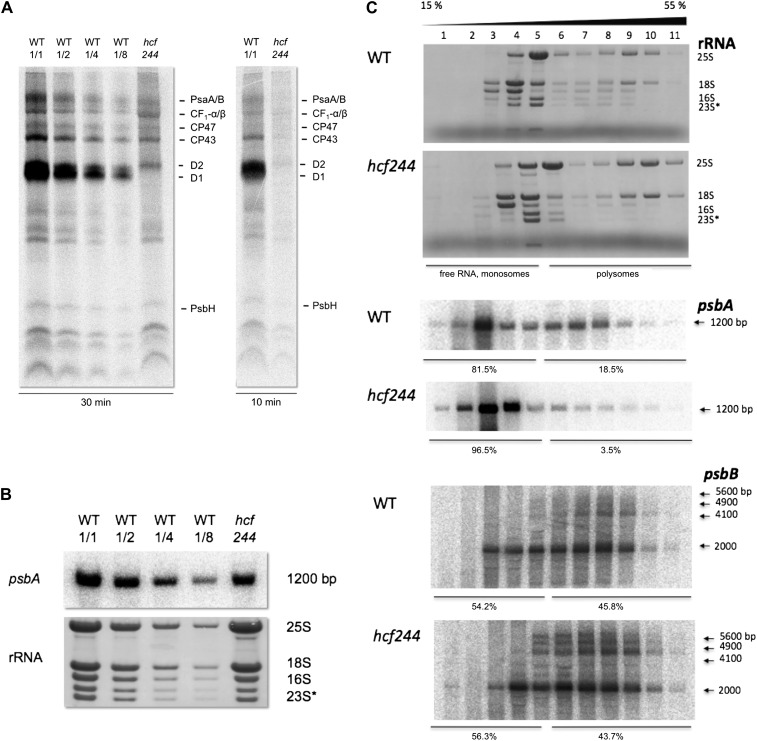
Figure 7.
Gene expression of psbA in wild-type (WT) and hcf244 mutant seedlings. A, In vivo labeling of newly synthesized membrane proteins by radioactive [35S]Met. Primary leaves of 2-week-old wild-type and hcf244 mutant plants were radiolabeled for 10 and 30 min. Subsequently, membrane proteins were isolated, separated by SDS-PAGE, and visualized by autoradiography. Lanes were loaded with an equivalent amount to 100,000 cpm (WT 1/1 and hcf244), 50,000 cpm (WT 1/2), 25,000 cpm (WT 1/4), and 12,500 cpm (WT 1/8). B, RNA gel-blot analyses of the psbA transcript from wild-type and hcf244 mutant plants. Total leaf RNA was isolated from 2- to 3-week-old plants. Lanes were loaded with 5 μg of total RNA or the indicated dilutions. The degradation product of the 23S rRNA is indicated by an asterisk. C, Polysome association studies in the wild type and the hcf244 mutant. Whole cell extracts of wild-type and hcf244 mutant plants were fractionated by linear 15% to 55% Suc gradients. Afterward, 11 equal fractions were harvested and extracted, and RNA was analyzed by RNA gel-blot hybridization. The distribution of rRNAs was visualized by methylene blue staining. The RNA amounts of psbA and psbB were detected by a specific probe and quantified by phosphor imaging.